2024 Email Authentication Standards: Elevating Security with Google and Yahoo
In contemporary email communication, email authentication plays a pivotal role in mitigating email fraud, spam, and phishing attacks. Brace yourself for a new level of security. Starting February 2024, Gmail and Yahoo will be implementing robust email authentication requirements to combat harmful messages and emphasize the crucial role of data security. This measure aims to prevent restrictions on sending rates, message blocking, and marking messages as spam.

Who will experience the effects?
The updated security guidelines apply to all users, particularly those who send 5000 or more than 5000 emails per day from ZOHO DESK. Not following these guidelines may lead to email delivery delays, blocked messages, or the categorization of emails as spam.
Not to worry. We are here to support you with the best possible solutions.
Basic details that every sender should be aware of
To safeguard your path in 2024, it is mandatory to follow the fundamental requirements, beginning with email authentications.
When utilizing a Gmail domain in the 'From' address, it is essential to configure the address with its dedicated SMTP for ensuring accurate mail delivery.
For recipients on gmail.com or googlemail.com, it is recommended to publish DMARC for the sender domain to enhance prompt mail delivery.
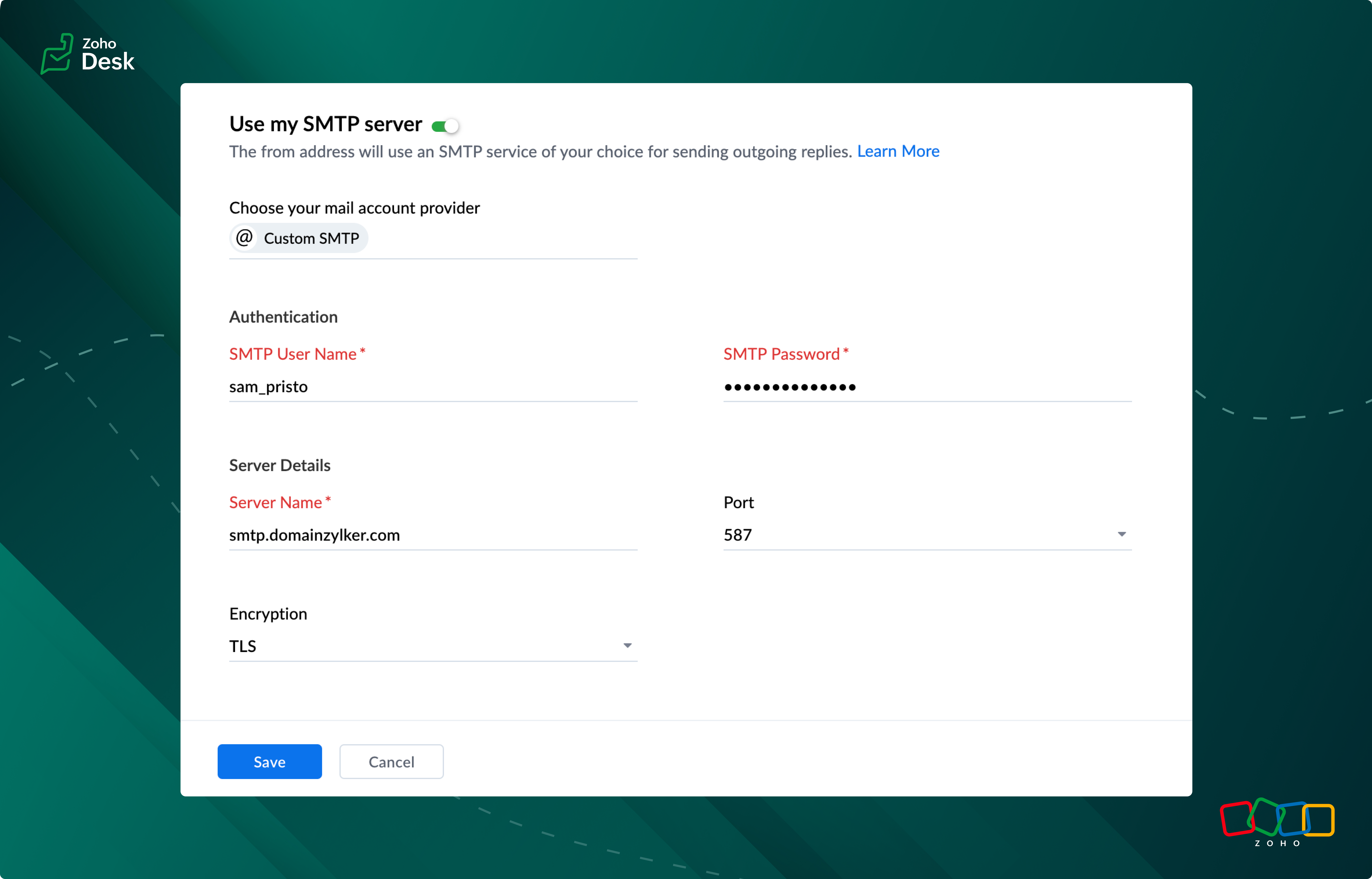
Verify with your own SMTP
In adherence to the new guidelines, reply emails sent from Zoho Desk with From addresses belonging to gmail.com, googlemail.com, to any domains may be bounced or marked as spam. Therefore, we kindly request all customers to configure these From addresses with your own SMTP verification and use TLS for transmitting email rather than Zoho SMTP. If the From addresses were verified previously with your own SMTP, we will continue using the same authentication for all notification emails sent from Zoho Desk.
Rolling out SPF & DKIM
SPF (Sender Policy Framework) and DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) are vital email authentication protocols that protect against spam, phishing, and spoofing. SPF verifies the authenticity of emails from your domain, while DKIM confirms their source by validating authorized servers associated with sending domains. These protocols work together to validate emails, ensuring that they originate from legitimate sources and have not been tampered with during transmission. This implementation enhances the overall security of your email communications by reducing the risk of email spoofing, phishing, and other malicious activities.
Minimal Spam Rate
Maintain spam rates below 0.10% and ensure they never exceed 0.30% for optimal email deliverability.
Essential Requirements for Users Sending 5000 or More Emails Daily
Implement DMARC Policy
DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication Reporting and Conformance) is an authentication technique that leverages the Sender Policy Framework (SPF) and DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM) to authenticate emails. This helps in preventing forging emails and engaging in unauthorized activities through them.
How DMARC Works:
1: Publish the DMARC policy outlining instructions for mailbox providers' receiving servers on how to handle emails that breach the policy.
2: Authenticate your sender domain by implementing SPF and DKIM.
3: The receiving server will apply the DMARC policy and execute the instructions specified in the policy.
4: The receiving server will send a report detailing how it handled the email to the reporting email address specified in the DMARC record.
Sample: DMARC record
v=DMARC1\; p=none\; rua=mailto:dmarc-aggregate@mydomain.com\; ruf=mailto:dmarc-afrf@mydomain.com\; pct=100
v: Signifies the DMARC version in use.
p: Signifies the policy established by the business.
rua: Specifies the URI for sending a consolidated report, including information on SPF and DKIM validation results, details about the sending and receiving domains, and the percentage of successful authentications.
ruf: Specifies the email address where the comprehensive SPF/DKIM failure report will be delivered.
pct: Denotes the percentage of emails subject to the policy application.
To prevent emails from being marked as spam, bounced, or experiencing delays in delivery, it is mandatory to set your policy (p) to none in DMARC record. “p = none”
 If the policy (p) is set to "quarantine" or "reject," the emails will either be redirected to the spam folder or will not be delivered to the recipient, respectively.
If the policy (p) is set to "quarantine" or "reject," the emails will either be redirected to the spam folder or will not be delivered to the recipient, respectively. Ensure DMARC Alignment
DMARC alignment pertains to the uniformity in the alignment of email authentication mechanisms, particularly SPF (Sender Policy Framework) and DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail), with the domain asserted by the sender.
Sample DMARC - SPF Alignment
Sender Address | From: Header | Strict Alignment | Relaxed Alignment |
support@mycompany.com | support@mycompany.com | Pass | Pass |
support@admin. mycompany.com | support@mycompany.com | Fail | Pass |
support@mycompany.org | support@mycompany.com | Fail | Fail |

SPF Strict Alignment: A precise match between the SPF-authenticated domain and the domain specified in the header's "From:" address.
SPF Relaxed Alignment: The domain indicated in the "From:" address of the header should either match or be a subdomain of the SPF-authenticated domain.
Sample DMARC - DKIM Alignment
From: Header | DKIM d= domain | Strict Alignment | Relaxed Alignment |
support@mycompany.com | mycompany.com | Pass | Pass |
support@admin. mycompany.com | mycompany.com | Fail | Pass |
support@mycompany.org | mycompany.com | Fail | Fail |

DKIM Strict Alignment: A precise match between the relevant DKIM domain and the domain specified in the header's "From:" address.
DKIM Relaxed Alignment: The domain mentioned in the "From:" address of the header must either coincide with or be a subdomain of the SPF-authenticated domain.
Add ARC headers
Implement ARC (Authenticated Received Chain) authentication to avoid Gmail categorizing the email as unauthenticated, especially when utilizing frequent mail forwarding practices.
For additional information on ARC authentication, please refer to the official Google document linked here.
Set up SPF & DKIM
Mail authentication protocols such as SPF & DKIM should be implemented for organization sending emails to google or yahoo recipients.
What are the consequences if the deadline is not met?
Adhering to the sender requirements before the deadline is crucial for optimizing email delivery. Failure to meet the criteria detailed in this article may lead to your email not reaching its destination as intended or being categorized as spam.
Quick Summary:
The Update - Gmail and Yahoo are implementing robust email authentication standards from February 2024.
The Effects - Failure to meet these requirements may result in emails being categorized as spam or not reaching their intended destination.
The Action to be taken - Users sending 5000 or more emails daily must implement SPF, DKIM and publish DMARC policies.
Regards,
Sumaya Howth - Product Manager
The Zoho Desk Team
Centralize Knowledge. Transform Learning.
All-in-one knowledge management and training platform for your employees and customers.
New to Zoho Recruit?
Zoho Developer Community
New to Zoho LandingPage?
Zoho LandingPage Resources
New to Bigin?
Topic Participants
Sumaya Howth
Stéphane LAMBERT
Jeff | Zoho Desk
Shivani | Zoho Desk
Sticky Posts
2024 Email Authentication Standards: Elevating Security with Google and Yahoo
In contemporary email communication, email authentication plays a pivotal role in mitigating email fraud, spam, and phishing attacks. Brace yourself for a new level of security. Starting February 2024, Gmail and Yahoo will be implementing robust emailUsing Agent Email Address as From Address
Currently, while replying to a ticket, it is possible for agents to choose their own email addresses as 'from' addresses. Although we built this just for that little extra flexibility, in hindsight, it hasn't figured much in conventional usage. Almost all businesses prefer that responses to their customers' tickets be sent from the common support/service email address and NOT from those of individual agents. During personal interactions at events, some of you have even made passing mentions aboutEdit and Delete options in Comments
A lot of teams have been using ticket comments extensively to collaborate everyday. Notification Center further improved this experience by bringing real-time updates. As we continue to build more improvements to this experience, we've shipped a small-yet-importantWebinar 2: Supercharged customer support for growing business
Join us for this webinar and learn how to step up your support game using a real-time communication platform to generate happier, more successful customers. In this live webinar, we will will discuss the importance of SalesIQ for your support team and how it can help you: Understand your customers better and their journeys to proactively support and engage them even before they ask for help. Integrating real time conversations into Zoho Desk’s Support, providing a conversational customer serviceCustomize Colors of your Customer Self Service Portal
You asked for it. We heard you. We're happy to roll out the most sought after feature request, Customizing the Colors of your Customer Self-service Portal. Now you can set the color of your customer portal to mimic your company's web site, so that your customers visiting the portal will not feel alienated by the default theme. Go ahead and configure the color of the header, tabs, fonts and background according to your needs. You can either choose between default color themes like Blue, Grey, Green
New to Zoho TeamInbox?
Zoho TeamInbox Resources
Zoho CRM Plus Resources
Zoho Books Resources
Zoho Subscriptions Resources
Zoho Projects Resources
Zoho Sprints Resources
Qntrl Resources
Zoho Creator Resources
Zoho CRM Resources
Zoho Show Resources
Get Started. Write Away!
Writer is a powerful online word processor, designed for collaborative work.
Zoho CRM コンテンツ
-
オンラインヘルプ
-
Webセミナー
-
機能活用動画
-
よくある質問
-
Ebook
-
-
Zoho Campaigns
- Zoho サービスのWebセミナー
その他のサービス コンテンツ
Nederlandse Hulpbronnen
ご検討中の方
Recent Topics
Zoho Subscriptions -- Zoho Commerce integration
Is there integration between Zoho Subscriptions and Zoho Commerce? I would like to create subscription plans in Zoho Subscritpions and list them for on my Zoho Commerce store.Synching changes to Stripe when changes are made in Zoho Billing
We have a situation where we have merged customers in Zoho BIlling and then found out later that the payment in Stripe was not updated and still associated with the old customer record. The card gets updated and billed, but that payment is still associatedHow can I link Products in a Deal Subform to the Products Module
Hello, I have a pricing subform on our Deals page and use a lookup field to associate a product with each line. I want to be able to look at a product page within the Products module and see a list of the deals connected to that product. I have this workingHelp Center and SEO: Any Benefit to My Domain-Mapped Website Ranking?
First of, I love the Help Center which I've just decided to integrate into my website to replace its old-fashioned FAQs. So much more to achieve there now! Lots of new benefits to the site visitors and to me in terms of organizing and delivering all theBusiness Hours with lunch break
Our business hours are: mon - fri 08:30 - 13:00, 15:00 - 18:30. How can I handle the lunch break? If I use 8:30 - 18:30 it obviously breaks SLA. ThanksZoho Desktop App- Unable to Minimize/Freezes
I'm having issues with my Zoho Mail desktop app (PC). When go on my desktop and open the app this is what happens: - Unable to minimize and close app (in the screenshot attached you can see at the top right there is no option to minimize/close) - UnableCan Zoho Marketing Automation send OTP codes via WhatsApp during user registration?
The flow I would like to implement is: A user signs up in the mobile app and enters their phone number. The system generates a one-time verification code (OTP). The OTP is sent to the user via WhatsApp message. The user enters the code in the app to confirmEnable Free External Collaboration on Notecards in Zoho Notebook
Hi Zoho Notebook Team, I would like to suggest a feature enhancement regarding external collaboration in Zoho Notebook. Currently, we can share notes with external users, and they are able to view the content without any issue. However, when these externalCan I export to PDF in Zoho Learn
I have seen help pages where export to pdf options are available but I do not see that option available from the application. I see that exprt is available in my free trial version but that is only to html pages. I need to be able to export my manualsZoho Commerce
Hi, I have zoho one and use Zoho Books. I am very interested in Zoho Commerce , especially with how all is integrated but have a question. I do not want my store to show prices for customers that are not log in. Is there a way to hide the prices if notZoho Sprints iOS app update: Global view, screen capture control, file encryption, tags enhancement
Hello everyone! We are excited to introduce new features in the latest version(v2.1) of the Zoho Sprints iOS app update. Let’s take a quick look at what’s new. 1. Global view Global view brings all your project items into one centralised space. You canMarking a meeting 'done'.
I would like to somehow mark a meeting 'done' and placed under the contact's page rather than deleting it and having no record of it. Am I missing a button that does this?Zoho Projects Android and iOS app update: Conditional layout rules for Tasks
Hello everyone! Task conditional layout rules configured on the web app(projects.zoho.com) are now applied on the Zoho Projects Android and iOS app. Conditional layout rules can be set for the Add/ edit task form and it allows you to change the propertyHow to account for vat with postponed VAT accounting
Hi everyone, looking for some help with postponed VAT accounting, I use DHL express for my imports and they used to pay the VAT for me and then invoice me. I could then log this as a bill and the VAT element from import was recorded as input VAT, allIntroducing Formula Fields for performing dynamic calculations
Greetings, With the Formula Field, you can generate numerical calculations using provided functions and available fields, enabling you to derive dynamic data. You can utilize mathematical formulas to populate results based on the provided inputs. ThisZobot with Plugs
Hello, I am having a problem with Zobot using Plugs. Here is my current flow: When I run the flow, I should immediately see the messages from the initial cards (Send Message cards), then after running the plug, and finally, see the messages after theUse URL field to populate Image in a Email Template
We have two records Record 1: Appointments (with a Lookup to Doctors module) Related Record 2: Doctors (with a URL field that is an image of the doctor) We would like to populate a CRM email template with the image of the URL field for the related doctorDelete button
Hi, The delete button were hide into the three dot button. Can I display outside? why Zoho make this update?Is there a way to show contact emails in the Account?
I know I can see the emails I have sent and received on a Contact detail view, but I want to be able to see all the emails that have been sent and received between all an Accounts Contacts on the Account Detail view. That way when I see the Account detailInvalid scope choice: Workdrive integration in CRM
Bug: There is an invalid option in the permission choices for Workdrive integration in CRM. If the entry "WorkDrive.teamfolder.CREATE" is selected, it will return a message indicating invalid OAuth scope scope does not exist.Dark Mode - Font Colors Don't Work
When editing a document in Dark Mode and selecting font colors, they don't show up on screen. Viewing/editing the same document in Light Mode shows them just fine.Good news! Calendar in Zoho CRM gets a face lift
Dear Customers, We are delighted to unveil the revamped calendar UI in Zoho CRM. With a complete visual overhaul aligned with CRM for Everyone, the calendar now offers a more intuitive and flexible scheduling experience. What’s new? Distinguish activitiesZoho mail admin panel not opening
Zoho CRM WooCommerce Integrtation
Looking for a solution for my 50 client to show detailed analytics on source of traffic that led to events, leads, conversions. Hi all, I have not been able to find a workable guide or solution to how exactly step by step integrate the Zoho CRM with WooCommerceAttaching files to emails within CRM Deals.
Hello, We have recently started using the extension "Workdrive for CRM" (Related List) to view/store our documents for each Deal, instead of using Attachments. Overall it feels like a better way to go but the user experience is not so great when it comesService line items
Hello Latha, Could you please let me know the maximum number of service line items that can be added to a single work order? Thanks, Chethiya.500 internal server error on opening an iframe through a deluge script
Hi Team I am trying to open an external url in an iframe through my deluge script which is associated to a custom button . By doing this i am getting an "Internal Server Error" . Please can you help me with this.Kaizen #225 - Making Query-based Custom Related Lists Actionable with Lookups and Links
Hello everyone! Welcome back to another post in the Kaizen series! This week, we will discuss an exciting enhancement in Queries in Zoho CRM. In Kaizen #190, we discussed how Queries bridge gaps where native related lists fall short and power custom relatedNo Need To Fix Something That Is Working
Zoho Books is a great financial tool which helps businesses to become more efficient and productive with day-to-day operations. As such, every change, upgrade, improvement needs to be carefully thought before implemented in the software and I'm sure ZohoFilter button in the Zoho Sheet Android App doesn't toggle on
I am a new Zoho Sheets user and experiencing a specific issue with the filter functionality in the Android mobile application. Detailed Issue Description: The filter icon appears correctly in the toolbar. Upon tapping the filter icon/button, the toggleIs Zoho Sites still actively being developed?
Hello, Is Zoho Sites still actively being developed as part of the Zoho ecosystem? I noticed that the What's New page (https://www.zoho.com/sites/whats-new.html) does not show any updates since Q1 2025. We were considering migrating our website from SquarespaceProject Notifcatiion Emails - Milestone
Hello: I cannot get myself, or most importantly my portal client user to recieve an email upon completion of a milestone. I have set up our 1st project. I have set up a test client user. (accepted the invitation and is listed in the system as a clientZoho Forms - Feature Request - Year Field
Hi Zoho Forms Team, You currently have the following date and time fields: Date Time Date and Time Year and Month It would be useful if you could include a "Year" field For example a recent application I completed said "What year was your house built?"Integrate Excel or Zoho Sheet functions / calculations to CRM product module
Hello Community, I hope someone more experienced can help me with this question. Our price / payment plan calculations are in an Excel spreadsheet and I would like to use all those functions / calculations in my Products module. So when we send a quoteSync CRM Contacts to USER'S contacts on Office 365
I can see that the O365 sync is transferring contacts backwards and forwards between Zoho CRM and Office365. But it has created a separate address book in Office 365 called "Zoho CRM Contacts". This address book is not used by Office/Outlook's email functionManage Every Customer Conversation from Every Channel inside Zoho SalesIQ
Your customers message you from everywhere. But are you really able to track, manage, and follow through on every conversation, without missing anything? With interactions coming in from websites, mobile apps, and messaging platforms like WhatsApp andZoho Books | Product updates | February 2026
Hello users, We’ve rolled out new features and enhancements in Zoho Books. From Advanced Reporting Tags to the ability to mark projects as completed, explore the latest updates designed to improve your bookkeeping experience. Introducing Advanced ReportingUpdate latitude & longitude address field API
How do I update the coordinates of an address field from a widget? I can't modify the latitude and longitude of the address field. I think the problem is how I'm writing formdata variable. zoho_init.then(function (data) { var queryParams = ZOHO.CREATOR.UTIL.getQueryParams();Zoho Forms - Feature Request - Past Into Scanning/OCR Field
Hi Zoho Forms Team, You recently introduced the OCR/Scanning field which I have found great use for with one client who receives work orders as a screenshot from one customer. I want to raise a feature request here which would make that field even moreinability to use different primary address on invoice per location
my company operates in two different locations with different email address. The problems then is the inability to edit the primary to suite the invoice for the second location.Next Page












