Kaizen #130 - Zoho CRM Scala SDK (V6) - Configuration and Initialization
Hello and welcome to another Kaizen week!
In this week's post, we'll show you how to get started with Zoho CRM's Scala SDK, and walk you through the configuration and initialization process. Specifically, we will discuss how to use the Scala SDK to make API calls authenticated via self-client. Please note that this article holds true for Scala SDK supporting version 6 of Zoho CRM APIs.
Software Development Kits (SDKs) are sets of tools and libraries designed to simplify the development process, and the integration between applications and specific platforms or services. They provide pre-built functionalities and abstract complex tasks, facilitating easier and faster development process. Zoho CRM's Scala SDKs act as a wrapper for the REST APIs, thus making it easier to use the services of Zoho CRM.
Simplified Authentication using Scala SDK
Authentication with Zoho CRM APIs is facilitated by the OAuth 2.0 protocol, ensuring secure access to its resources. The process begins with the generation of a grant token for your organization in the Zoho Developer Console, where you specify the required scopes. Subsequently, using this grant token, you can generate both the access token, used for API call authentication, and the refresh token, employed for refreshing the access tokens after their one-hour expiry period. You must persist these tokens, along with their expiry times, in your server's data store for seamless API access.
However, with the Scala SDK, this authentication process is significantly simplified. After generating the grant token and initialization, the SDK takes care of the rest. The SDK handles token generation, persistence, and refreshing the access token automatically, ensuring access to the resources without manual intervention.
Using the Zoho CRM Scala SDK
Before diving into the usage of Scala SDKs, ensure that the following prerequisites are met:
- Ensure that the client app has Java version 11 or above.
- Ensure that the client app has Scala version 2.13.5 or above.
- Have an IDE such as IntelliJ installed.
- An active Zoho CRM account.
1. Register your application with Zoho CRM
When you register a client with Zoho CRM, you establish a connection between your application and Zoho CRM, enabling your application to securely access and interact with Zoho CRM APIs and resources after authentication. The registration process involves providing essential details such as the client type, homepage URL, and authorized redirect URIs, depending on the type of client you choose.
To register your client:
- Go to the Zoho Developer Console
- Click on Get Started or +ADD CLIENT
- Choose the Client Type as Self-Client or Server based Applications depending on your application. Read our Kaizen post on the different client types to understand better. For this article, we will proceed with Self-client as we aim to develop a Scala application for our own use.
- Fill in the necessary details and click CREATE to register your client successfully. This will provide you with a Client ID and Client Secret.

2. Create a Scala project in your preferred IDE
If you already have your project set up, you may skip this step. However, if you are starting out, the next crucial step is to create a Scala Project in your preferred IDE. For the purpose of this guide, we will be using IntelliJ IDEA as the IDE of choice.
3. Include the Zoho CRM Scala SDK in your project
To include the Zoho CRM Scala SDK in your project, you can follow different methods as outlined here. However, for the purpose of this guide, we will demonstrate how to include the SDK using the build.sbt file.
Follow these steps to include the Zoho CRM Scala SDK in your project using the build.sbt file:
- Open your project in IntelliJ IDEA or your preferred IDE.
- Locate the build.sbt file in your project directory.
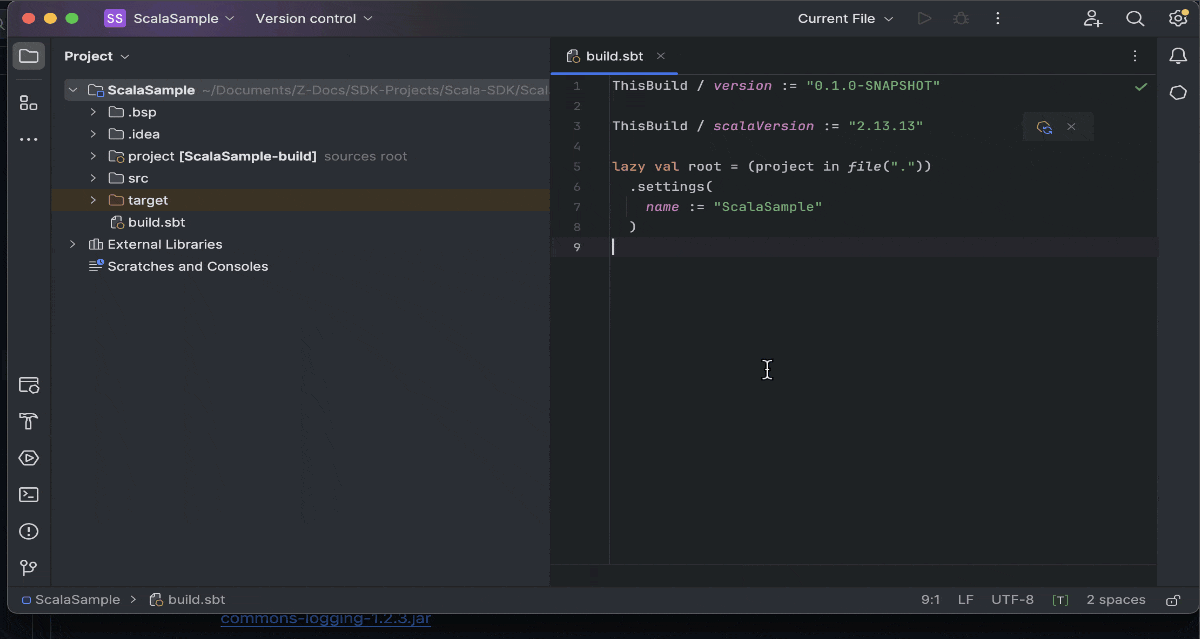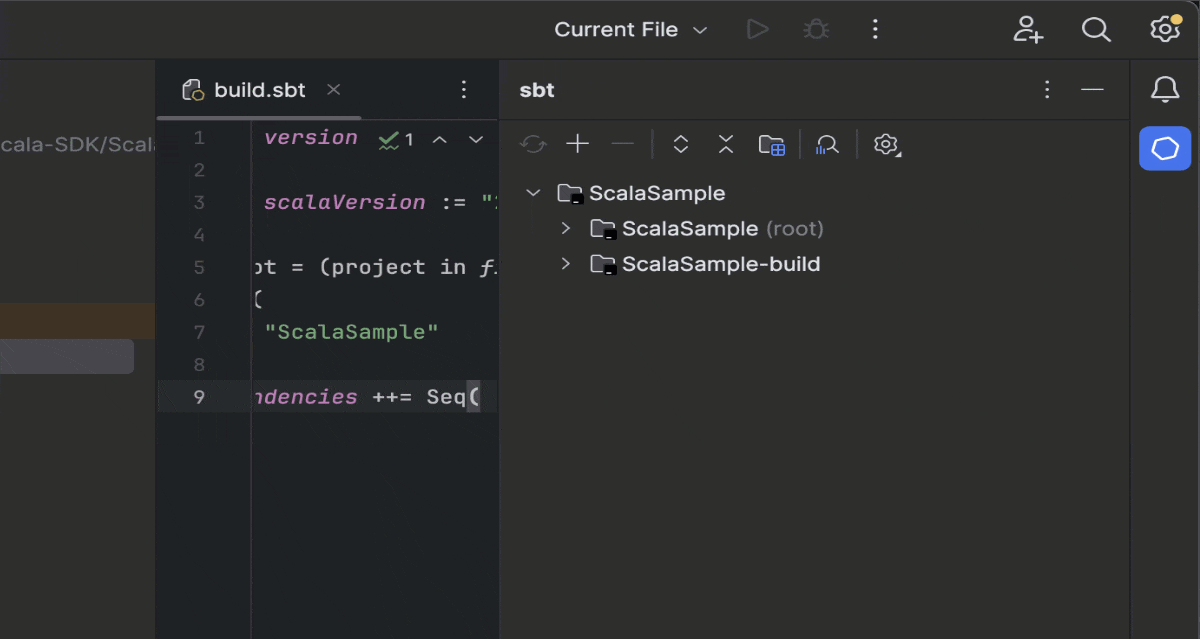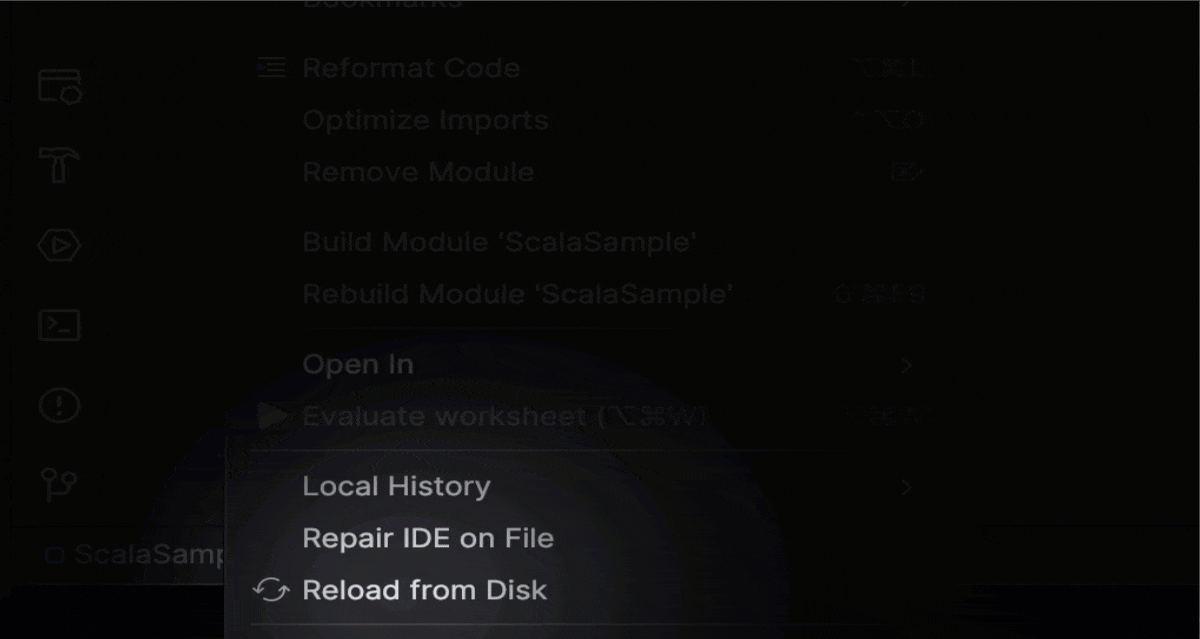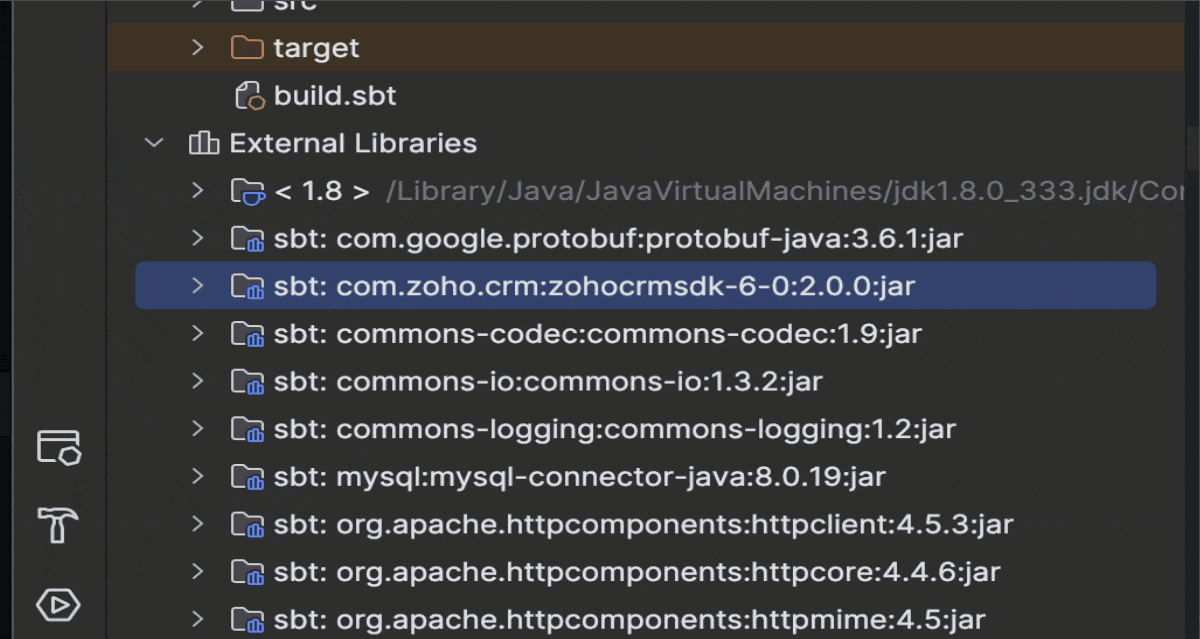
- Add the Zoho CRM Scala SDK dependency to your build.sbt file. To add the latest version (supporting version 6 of Zoho CRM APIs), include this line in the file and Save: libraryDependencies ++= Seq( "com.zoho.crm" % "zohocrmsdk-6-0" % "2.0.0")
- Sync the changes and reload the files to ensure that the SDK has been added to the project.
Please note that when you install the Zoho CRM SDK, there are many dependencies which will also be installed. These dependencies are necessary for the proper functioning of the SDK and will be automatically managed by your build tool (such as sbt) during the installation process.
4. Obtain the grant token to authenticate your client
To make API calls, you need to authenticate your client by generating a grant token with the required scopes. For this guide, we will be using the self-client created in the first step.
Log in to the Zoho Developer Console, and generate the grant token with the required scopes. Please note that this grant token has a short life span, and that it is used to generate the access and refresh tokens. Refer to our Kaizen on OAuth2.0 for more details.
5. Configuration and Initialization of the SDK
The configuration step in initializing the SDK involves setting up various objects to define how the SDK operates. This includes specifying the domain for API calls, token persistence, error logging, resource information storage, and more.
Before going into the specifics of various configurations, let us first discuss Token Persistence. Token Persistence refers to the mechanism through which access tokens and refresh tokens obtained during authentication are stored and managed by the SDK. By storing tokens securely, the SDK can automatically manage token expiration and renewal, eliminating the need for manual token handling by the developer.For details on the different persistence methods supported by our SDKs, please refer to the last section of this post. In this guide, we will be using File Persistence as the method for Token Persistence. However, please note that users must choose the method that best suits their requirements and preferences.
Here is a sample code to initialize the SDK. Make sure to replace the client ID, client secret, grantToken, file paths, and other configurations with your specific values.
- import com.zoho.api.authenticator.OAuthToken
- import com.zoho.crm.api.dc.USDataCenter
- import com.zoho.crm.api.exception.SDKException
- import com.zoho.crm.api.{HeaderMap, Initializer, SDKConfig}
- import com.zoho.api.logger.Logger
- import com.zoho.api.authenticator.store.FileStore
- object BulkWrite {
- @throws[SDKException]
- def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
- val environment = USDataCenter.PRODUCTION
- val token = new OAuthToken.Builder().clientID("1000.xxx").clientSecret("xxx").grantToken( "1000.xxx").findUser(false).build()
- //Object containing the absolute file path to store tokens
- var tokenstore = new FileStore("/Documents/SDK-Projects/Scala-SDK/ScalaSample/sdk_tokens_new.txt")
- var logger = new Logger.Builder()
- .level(Logger.Levels.ALL)
- .filePath("/Documents/SDK-Projects/Scala-SDK/ScalaSample/scala_sdk_log.log")
- .build
- var sdkConfig = new SDKConfig.Builder().pickListValidation(false).autoRefreshFields(false).connectionTimeout(1000).requestTimeout(1000).socketTimeout(1000).build
- new Initializer.Builder().environment(environment).token(token).store(tokenstore).logger(logger).SDKConfig(sdkConfig).initialize()
- }
- }
- class BulkWrite {}
During the initialization step, the following configuration details have to be defined to configure the behavior and functionality of the SDK. While two of them are mandatory, the others are optional.
- environment (mandatory): It determines the API environment, which dictates the domain and URL for making API calls. The format follows the Domain.Environment pattern.
eg : val env = USDataCenter.PRODUCTION - token (mandatory) : Contains the user token details. Create an instance of OAuthToken with the details that you get after registering your Zoho client. Depending on the available tokens, you can select one of the following flows:
- Grant Token Flow: Involves storing and persisting the grant token. This flow is used when you have a grant token available. The SDK will generate and persist the access and refresh tokens, and also refresh the access token upon expiry.
- Refresh Token Flow: Involves storing and persisting the refresh token. This flow is used when you have a refresh token available. The SDK will generate and persist the access and refresh tokens, and also refresh the access token upon expiry.
- Access Token Flow: In this flow, the access token is directly utilized for API calls without token persistence. The SDK will persist the access token, but upon expiry it won't be refreshed, and an INVALID_TOKEN error will be thrown once the access token has expired.
- Id FLow : You can use the id from the persisted token file/DB to make API calls. The id is a unique system generated value for each token details entry in the file/DB. Please note that you can use this method only after the SDK has already been initialized.
- logger (optional) : You can customize the logging behavior by setting the desired log level, which can be one of the following: FATAL, ERROR, WARNING, INFO, DEBUG, TRACE, ALL, or OFF. Additionally, you can configure the file path and file name for the log file.
- store (optional) : Allows you to configure token persistence for your application. If this is skipped, the SDK will create the "sdk_tokens.txt" file in the current working directory by default to persist the tokens.Database PersistenceFile PersistenceCustom Persistencevar tokenstore = new DBStore.Builder().host("hostName").databaseName("databaseName").tableName("tableName").userName("userName").password("password").portNumber("portNumber").buildvar tokenstore = new FileStore("/Users/user_name/Documents/scala_sdk_token.txt")var tokenStore = new CustomStore()
- SDKConfig (optional) : This method takes care of additional SDK configurations.Configuration KeyDescriptionautoRefreshFieldsDefault Value : FalseA boolean configuration field to enable or disable automatic refreshing of module fields in the background. If set to true, fields are refreshed every hour, and if set to false, fields must be manually refreshed or deleted.pickListValidationDefault Value : TrueThis field enables or disables pick list validation. If enabled, user input for pick list fields is validated, and if the value does not exist in the pick list, the SDK throws an error. If disabled, the input is not validated and the API call is made.enableSSLVerificationDefault Value : TrueA boolean field to enable or disable curl certificate verification. If set to true, the SDK verifies the authenticity of certificate. If set to false, the SDK skips the verification.connectionTimeoutDefault Value : 0The maximum time (in seconds) to wait while trying to connect. Use 0 to wait indefinitely.timeoutDefault Value : 0The maximum time (in seconds) to allow cURL functions to execute. Use 0 to wait indefinitely.
- requestProxy (optional) : Configure this only if you're using a proxy server to make the API calls. To configure, create an instance of RequestProxy containing the proxy properties of the user.var requestProxy = new RequestProxy.Builder().host("proxyHost").port(80).user("proxyUser").password("password").userDomain("userDomain").build()
- resourcePath (optional) : To configure the absolute directory path to store user-specific files containing module fields information. If this object is skipped, the files will be stored in the project directory itself.
Once the initialization is successful, you can verify that the access and refresh tokens are generated and persisted. You can do this by checking the tokens file or the database, depending on the token persistence method you configured during initialization.
Token Persistence
There are three token persistence methods supported by our SDKs.
- Token Persistence using a Database : In Database persistence, tokens are stored and retrieved from a database (e.g., MySQL). In this case, you should create a table in your database with the required columns. The custom database name and table name can be set in DBStore instance, when you initialise the SDK.For instance, to persist your tokens in a table named token in database named zoho in your mySQL DB, use this:CREATE DATABASE zoho; // use this to create database named zoho// use this to create a table named token, with the following necessary columnsCREATE TABLE token (id varchar(10) NOT NULL,user_name varchar(255) NOT NULL,client_id varchar(255),client_secret varchar(255),refresh_token varchar(255),access_token varchar(255),grant_token varchar(255),expiry_time varchar(20),redirect_url varchar(255),
api_domain varchar(255),primary key (id)); - File Persistence : This method allows storing and retrieving the authentication tokens from the file in the file path that you configure. The file will contain the id, user_name, client_id, client_secret, refresh_token, access_token, grant_token, expiry_time, redirect_url, and api_domain.
- Custom Persistence : This is a method where users can create their own method of storing and retrieving authentication tokens. To use this method, users need to implement the TokenStore interface and override its methods according to their own logic. For more details, please refer here.
We hope that you found this useful. In next week's Kaizen post, we will discuss about Bulk Write operations using the Scala SDK for Zoho CRM, and on how to import both parent and child records in a single operation.
If you have any queries, let us know the comments below, or send an email to support@zohocrm.com. We would love to hear from you.
Cheers!
Anu Abraham
Anu Abraham

Recommended Reads:
- Check out our Kaizen Collection here
- Zoho CRM SDKs
- Scala SDK - Github
- Client Types in Zoho API Console
- Previous Kaizen : Client Script Support for Blueprints
Centralize Knowledge. Transform Learning.
All-in-one knowledge management and training platform for your employees and customers.
New to Zoho Recruit?
Zoho Developer Community
New to Zoho LandingPage?
Zoho LandingPage Resources
New to Bigin?
Topic Participants
Anu Abraham
Sticky Posts
Kaizen #198: Using Client Script for Custom Validation in Blueprint
Nearing 200th Kaizen Post – 1 More to the Big Two-Oh-Oh! Do you have any questions, suggestions, or topics you would like us to cover in future posts? Your insights and suggestions help us shape future content and make this series better for everyone.Kaizen #226: Using ZRC in Client Script
Hello everyone! Welcome to another week of Kaizen. In today's post, lets see what is ZRC (Zoho Request Client) and how we can use ZRC methods in Client Script to get inputs from a Salesperson and update the Lead status with a single button click. In thisKaizen #222 - Client Script Support for Notes Related List
Hello everyone! Welcome to another week of Kaizen. The final Kaizen post of the year 2025 is here! With the new Client Script support for the Notes Related List, you can validate, enrich, and manage notes across modules. In this post, we’ll explore howKaizen #217 - Actions APIs : Tasks
Welcome to another week of Kaizen! In last week's post we discussed Email Notifications APIs which act as the link between your Workflow automations and you. We have discussed how Zylker Cloud Services uses Email Notifications API in their custom dashboard.Kaizen #216 - Actions APIs : Email Notifications
Welcome to another week of Kaizen! For the last three weeks, we have been discussing Zylker's workflows. We successfully updated a dormant workflow, built a new one from the ground up and more. But our work is not finished—these automated processes are
New to Zoho TeamInbox?
Zoho TeamInbox Resources
Zoho CRM Plus Resources
Zoho Books Resources
Zoho Subscriptions Resources
Zoho Projects Resources
Zoho Sprints Resources
Qntrl Resources
Zoho Creator Resources
Zoho CRM Resources
Zoho Show Resources
Get Started. Write Away!
Writer is a powerful online word processor, designed for collaborative work.
Zoho CRM コンテンツ
-
オンラインヘルプ
-
Webセミナー
-
機能活用動画
-
よくある質問
-
Ebook
-
-
Zoho Campaigns
- Zoho サービスのWebセミナー
その他のサービス コンテンツ
Nederlandse Hulpbronnen
ご検討中の方
Recent Topics
Zoho Creator In-App Notification
Hi Team, I have implemented an in-app notification using code, as it required some customization. I followed the example in the link below: https://www.zoho.com/deluge/help/pushnotify-using-deluge.html#Example I have a couple of questions regarding thisRestrict portal signup until registration form and payment are completed
Hi everyone, I am working on a Zoho Creator portal for a project. In our business flow, users must first fill out a registration form and pay a registration fee before they are allowed to access the portal. However, when I share the portal link, usersHow to install Widget in inventory module
Hi, I am trying to install a app into Sales Order Module related list, however there is no button allow me to do that. May I ask how to install widget to inventory module related list?Add Lookup Field in Tasks Module
Hello, I have a need to add a Lookup field in addition to the ones that are already there in the Tasks module. I've seen this thread and so understand that the reason lookup fields may not be part of it is that there are already links to the tables (CRM x WorkDrive: File storage for new CRM signups is now powered by WorkDrive
Availability Editions: All DCs: All Release plan: Released for new signups in all DCs. It will be enabled for existing users in a phased manner in the upcoming months. Help documentation: Documents in Zoho CRM Manage folders in Documents tab Manage filesUnable to integrate Zoho Projects and Zoho Workdrive
I'm a Zoho One subscriber. When I go to Zoho Projects > Settings > Marketplace > Zoho Apps I do not see an option for Zoho Workdrive but I do see one for Zoho Docs that does nothing. How do I get the option to integrate Zoho WorkDrive and Zoho ProjeUpload own Background Image and set Camera to 16:9
Hi, in all known online meeting tools, I can set up a background image reflecting our corporate design. This doesn't work in Cliq. Additionally, Cliq detects our cameras as 4:3, showing black bars on the right and left sides during the meeting. Where【まだ間に合う!】Zoho ユーザー交流会 | AI活用・CRM・Analytics の事例を聞いて、ユーザー同士で交流しよう!
ユーザーの皆さま、こんにちは。コミュニティチームの藤澤です。 3月27日(金)に東京、新橋で開催する「東京 Zoho ユーザー交流会 NEXUS」へのお申し込みがまだの方は、この機会にぜひお申し込みください!(参加無料) ーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーー イベントの詳細はこちらから▷▷ https://www.zohomeetups.com/tokyo2026vol1#/?affl=communityforumpost3 ーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーーZeptoMail API
Hello Since today, we experience issues with the ZeptoMail API. When trying to send e-mails using: https://api.zeptomail.eu/v1.1/email we receive the error: (503) Site unavailable due to a traffic surge. Please try again shortly. I kindly ask you to identifySender Email Configuration Error.
Hello Team, Hope you are all doing well. We are in the process of creating the Zoho FSM environment in the UAE. When we try to add the sender email address “techsupportuae@stryker.com”, we receive the error message: “Error occurred while sending mailManaging user mailbox actions
An organization often has users with different roles and responsibilities, such as leadership, operations, or support teams. While some users may require full access to email features, others may only need limited functionality. For example, enablingSuper Admin Logging in as another User
How can a Super Admin login as another user. For example, I have a sales rep that is having issues with their Accounts and I want to view their Zoho Account with out having to do a GTM and sharing screens. Moderation Update (8th Aug 2025): We are workingCustom function return type
Hi, How do I create a custom deluge function in Zoho CRM that returns a string? e.g. Setup->Workflow->Custom Functions->Configure->Write own During create or edit of the function I don't see a way to change the default 'void' to anything else. AddingInternal Fillable Contract with Zoho Writer (Before Sending to Client)
Hi everyone, I’m trying to automate the following process in Zoho CRM and would appreciate some guidance. Process: When a Deal moves to a specific stage, CRM triggers an automation. CRM sends a contract template to an internal team member so they canUpdate P_Leave: code: 7052 "Employee_ID": "Enter Employee ID"
Hi, Zoho People - Update Leaves Can someone assist? ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ col = Collection(); col.insert("recordid":id); col.insert("Date_Check_Approval":zoho.currentdate); info zoho.people.update("P_Leave",col.toMap());Prevent tracking users from specific countries
Currently, I’m receiving many bot visits from the United States and Malaysia. I would like these visits not to be recorded in SalesIQ. I already enabled the option to exclude traffic from cloud service providers, but I’m still receiving bot visits. Ideally,Print a document from Zoho Writer via Zoho Creator
If i use the code below i can get writer to create a new document or email it to me but i want to be able to print it directly from the browser and not have to send it via email and then print. Below is the code im using. Attached options form zoho writerEs posible cambiar el lenguaje de los modulos del ASAP?
Es posible cambiar el lenguaje de estos textos? Tengo Zoho configurado en español pero aun así me muestra estos textos en ingles:System Components menu not available for Tablet to select language
I have attached a screenshot of my desktop, mobile, and tablet menu builder options. I am using 2 languages in my application. Language Selection is an option under the System Components part of the menu, but only for my desktop and phone(mobile). MyUsing workflows to automatically set classification of new tickets
Hello, I am trying to use a workflow to set a classification for a new ticket that is created via an email coming into my desk department. The workflow is working fine if I create a ticket from within desk, however if a ticket is emailed in then thisText/SMS With Zoho Desk
Hi Guys- Considering using SMS to get faster responses from customers that we are helping. Have a bunch of questions; 1) Which provider is better ClickaTell or Screen Magic. Screen Magic seems easier to setup, but appears to be 2x as expensive for United States. I cannot find the sender id for Clickatell to even complete the configuration. 2) Can customer's reply to text messages? If so are responses linked back to the zoho ticket? If not, how are you handling this, a simple "DO NOT REPLY" asDefault/Private Departments in Zoho Desk
1) How does one configure a department to be private? 2) Also, how does one change the default department? 1) On the list of my company's Zoho Departments, I see that we have a default department, but I am unable to choose which department should be default. 2) From the Zoho documentation I see that in order to create a private department, one should uncheck "Display in customer portal" on the Add Department screen. However, is there a way to change this setting after the department has been created?Show unsubscribed contacts ?
Hello, I would like to display the unsubscribed contacts. Unfortunately, I do not have this subscription type as described in the documentation (https://help.zoho.com/portal/en/kb/marketing-automation-2-0/user-guide/contacts/contact-management/articles/subscription-type-24-1-2024#Subscription_Type_field.)Can Zoho Marketing Automation send OTP codes via WhatsApp during user registration?
The flow I would like to implement is: A user signs up in the mobile app and enters their phone number. The system generates a one-time verification code (OTP). The OTP is sent to the user via WhatsApp message. The user enters the code in the app to confirmWhat's New in Zoho Inventory | Q2 2025
Hello Customers, The second quarter have been exciting months for Zoho Inventory! We’ve introduced impactful new features and enhancements to help you manage inventory operations with even greater precision and control. While we have many more exciting"Spreadsheet Mode" for Fast Bulk Edits
One of the challenges with using Zoho Inventory is when bulk edits need to be done via the UI, and each value that needs to be changed is different. A very common use case here is price changes. Often, a price increase will need to be implemented, andCloning Item With Images Or The Option With Images
Hello, when I clone an item, I expect the images to carry over to the cloned item, however this is not the case in Inventory. Please make it possible for the images to get cloned or at least can we get a pop up asking if we want to clone the images asZOHO BOOKS - RECEIVING MORE ITEMS THAN ORDERED
Hello, When trying to enter a vendor's bill that contains items with bigger quantity than ordered in the PO (it happens quite often) - The system would not let us save the bill and show this error: "Quantity recorded cannot be more than quantity ordered."Stock count by bin location
Is there a configuration to make a stock count by bin or area and not by product. these is useful to manage count by area RegardsServer-based Appication API access for Social, Sites, Flow, Pages.
Hello, I am trying to hook up API access for a number of apps and I have hit a wall trying to add these scopes to the API feed. We cannot find the correct way to list the scope for these Zoho apps; Social, Sites, Flow, Writer. Error on web-page comesFeature Request: "Send Invitation" Toggle for Events
I am writing to request a critical "Quality of Life" update for the Activities module. Currently, adding people to the Participants field in an Event triggers an automatic email invitation/acceptance tracking with no way to opt-out. For general eventsZoho Survey: Bulk Exporting Raw Data (CSV/Excel) from 100+ Individual Survey Projects
Hi Zoho Community, I am currently managing a 360-degree evaluation process that involves 100+ individual survey projects (one separate survey for each employee being evaluated). I need to download the raw response data (CSV or Excel) for all 100 surveys.Zoho Survey – Page Skip Logic Not Working
Hi everyone, I'm experiencing an issue with the page skip logic in Zoho Survey. Last week, it was working fine, and I haven’t changed anything in the settings. However, today the skip logic is not working at all. I also tried testing it with differentBrand Studio Projects in Analytics
Hi All, Currently pulling my hair out over trying to link together some social media posts for a reporting dashboard in Analytics, so I thought I'd see if anyone on here had a solution. Our Marketing Team created a LinkedIn campaign in Zoho Brand Studio,ERROR: Product type cannot be changed for Items having transactions.
I have mistakenly added a product type as goods for an item that was a digital service. Now when HSN/SAC became mandatory, this brought my attention to this error I did. So I tried changing the product type but it displayed this error message ProductCombine and hide invoice lines
In quickbooks we are able to create a invoice line that combines and hides invoices lines below. eg. Brochure design $1000 (total of lines below, the client can see this line) Graphic Design $600 (hidden but entered to reporting andAnyone worked out how to export or screengrab a full heatmap?
I'd love to be able to include a copy of a heatmap in a report but can't work out how to grab the whole thing as there doesn't appear to be an export function? Thanks in advance.Introducing Built-in Telephony in Zoho Recruit
We’re excited to introduce Built-in Telephony in Zoho Recruit, designed to make recruiter–candidate communication faster, simpler, and fully traceable. These capabilities help you reduce app switching, handle inbound calls efficiently, and keep everyAuto-publish job openings on my Zoho Recruit Careers Website
I have developed a script using the Zoho Recruit API that successfully inserts new jobOpening records to my Zoho Recruit website, but my goal is to auto-publish to the Careers Website. The jobOpening field data shows two possible candidates to make this[Free webinar] Custom domains for portals in Zoho Creator - Creator Tech Connect
Hello everyone, We’re excited to invite you to another edition of the Creator Tech Connect webinar. About Creator Tech Connect The Creator Tech Connect series is a free monthly webinar featuring in-depth technical sessions designed for developers, administrators,Next Page












