Visualize Charts Using Groupby and Aggregate functions
Hello!
Have you been using tables to present data in mail merged documents? If so, it maybe time to try a more interesting alternative. Charts help you present data in an exciting way, and make it easy to highlight specific aspects of your data.
With Writer, adding charts to mail merged documents is simple. Easily create and edit charts to meet your needs using different chart types, built-in aggregation functions, and chart customization options.
Aggregation in charts / Aggregate functions in charts
Pull data from your data source and choose an aggregate function to present it within your document. Writer offers Count, Count Distinct, Sum, Average, Min, Max, and Median functions to process your data however you need.
1. Numerical data aggregation
Data comprised entirely of numbers (such as the number of cars sold by a company) is numerical data. Compared with raw or individual data (like a list of all cars sold), aggregated data (such as the number of a specific type of car sold every month) is more useful. Writer helps you instantly aggregate data with built-in chart functions.
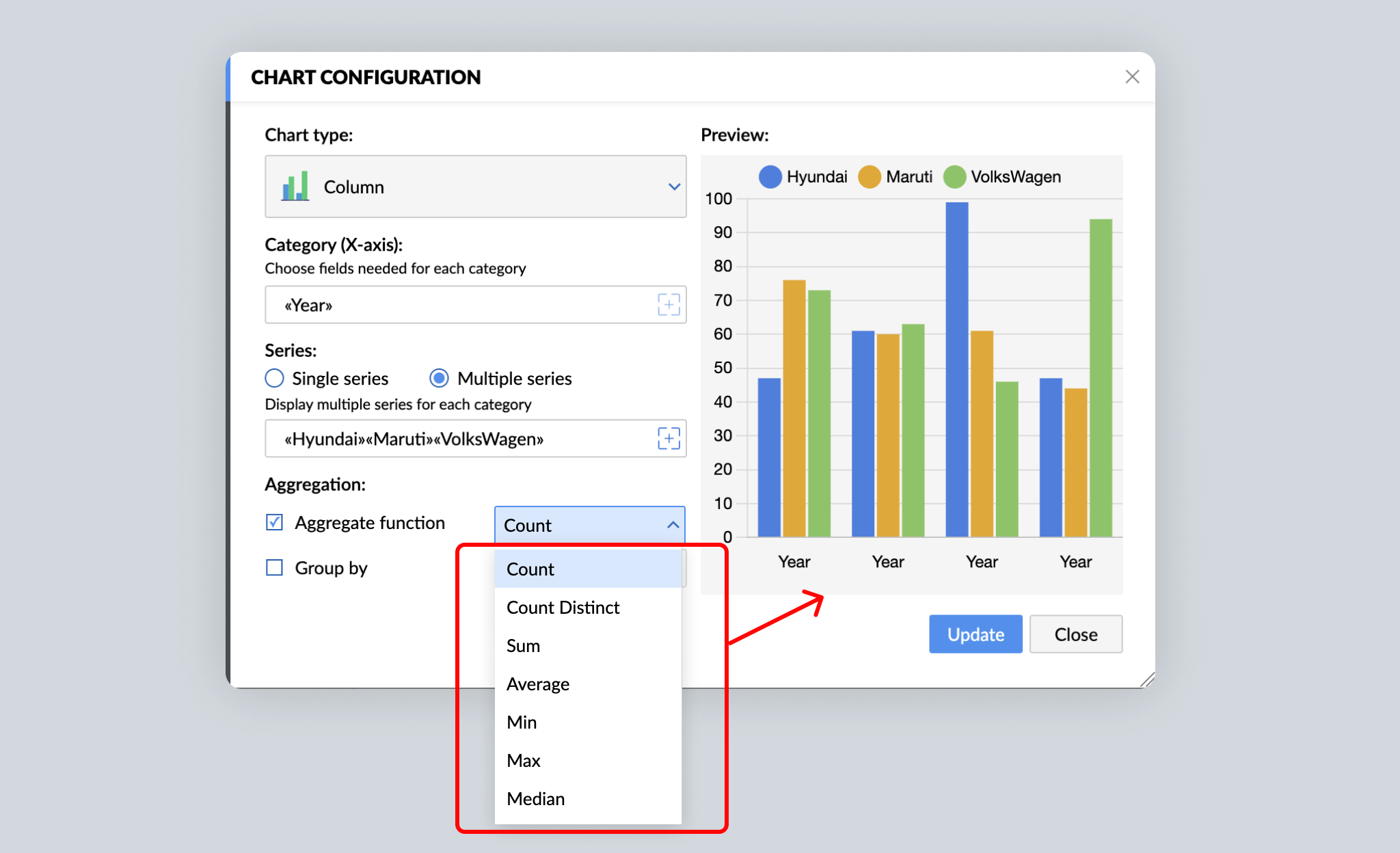
Writer's charts support the following aggregate functions: Count, Count Distinct, Sum, Average, Min, Max, and Median. For example, you can apply the Count function to the monthly sales data to get the number of cars sold per month. Similarly, the Average function will show the average number of sales per month. Click here to learn what each aggregation function does.
Aggregated data helps reveal patterns, and charts make the patterns easy to understand. In the case of our example, a chart provides an overview of the car company's monthly sales performance.
2. Non-numerical data aggregation
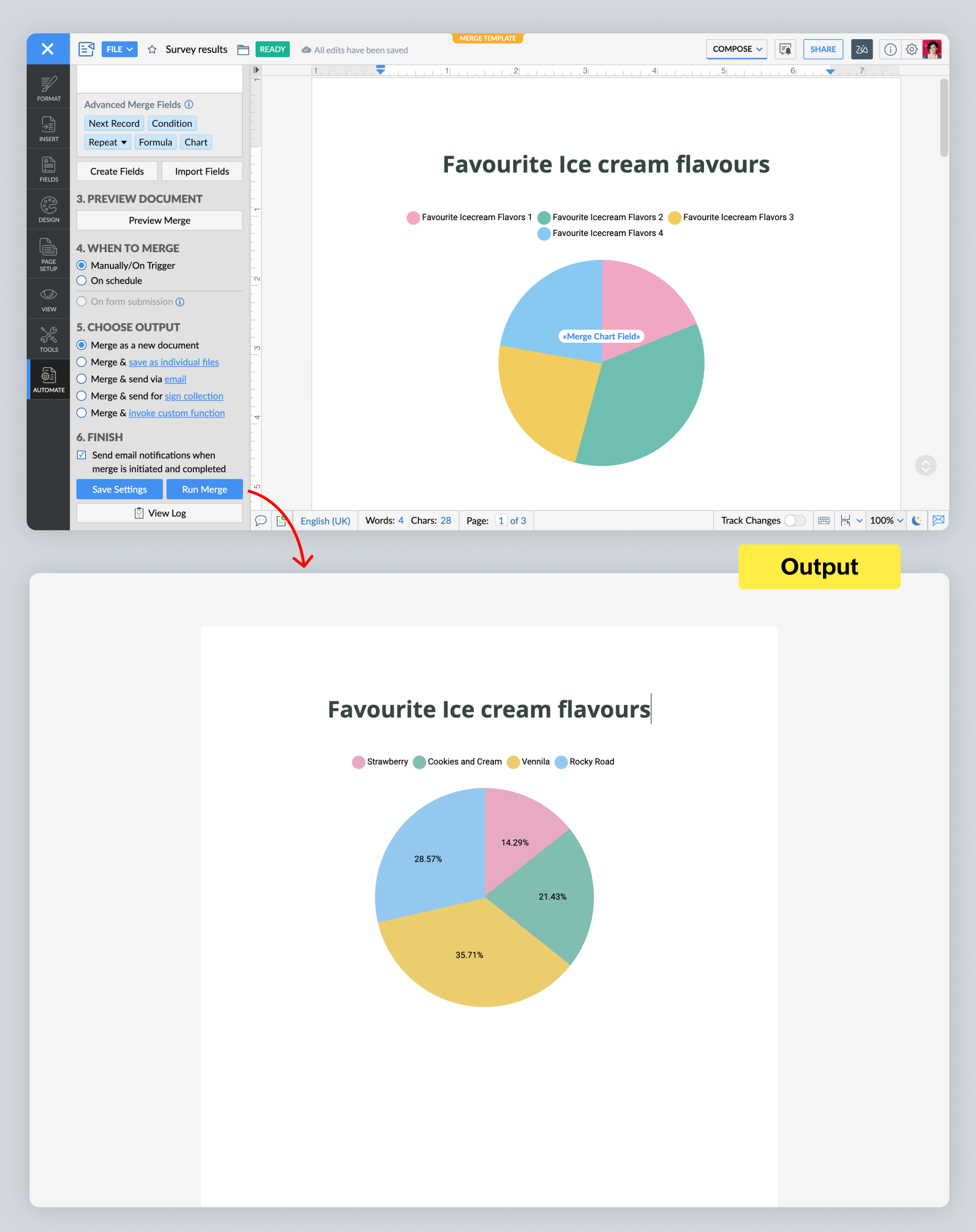
Any data without numbers (such as yes/no answers, or answers to open-ended questions) is non-numerical data. Let's say a fast food restaurant wants to add ice cream to its menu. It can run a survey among its customers asking for their favorite ice cream flavors. From there, it can use Writer to aggregate the responses, and present them in the form of a pie chart to easily understand customers' preferences.
3. Group By and Aggregate
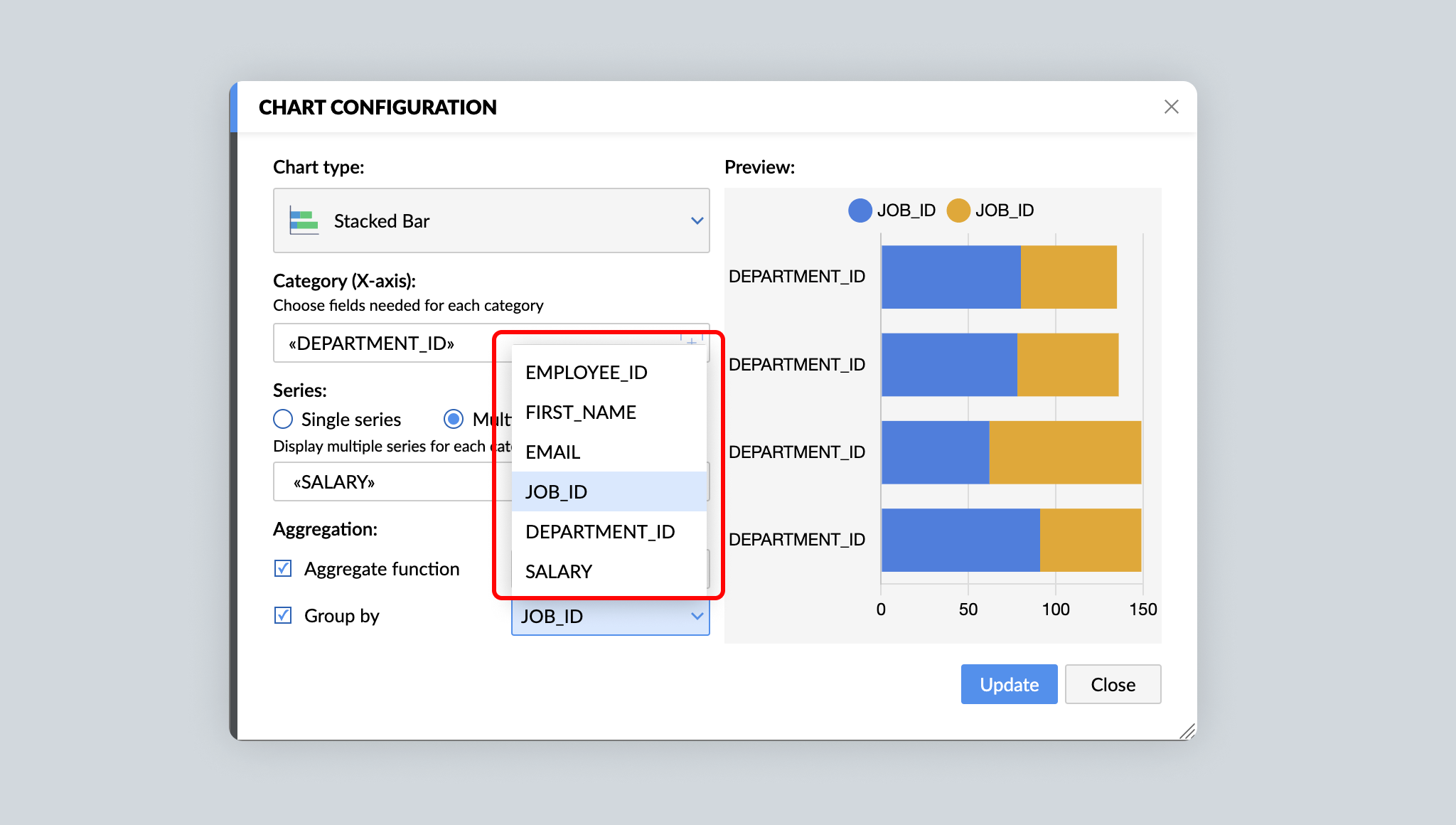
For detailed analysis and insights, you may choose to split data into separate groups before aggregating them. For example, in addition to the total number of cars sold in a month, you might also want to know the number of hatchbacks, sedans, and coupes sold in a month. With Writer's Group By function in charts, segregating raw data into different groups and then aggregating them becomes simpler.
Advanced chart tools
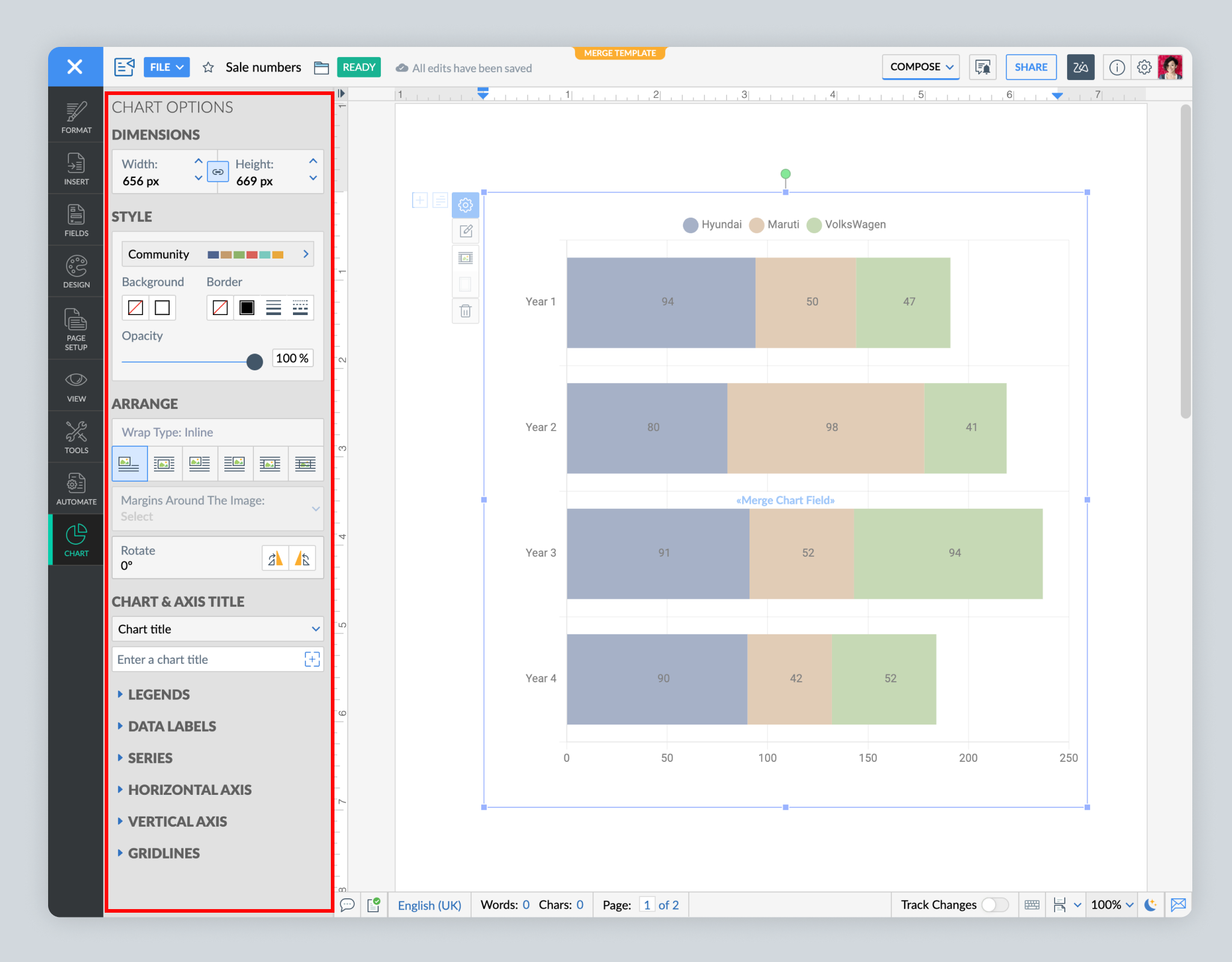
Make your data visually appealing and easy to understand. After choosing a chart type, use various customization options, such as colors, wrap style, margins, position of legends and data labels, and font sizes.
That's all for now! Tryout Writer's charts, advanced chart tools, and aggregate functions in mail merge, and let us know what you think.
Need any help working with charts? Write to us at support@zohowriter.com or simply leave a comment.
Happy writing!
Centralize Knowledge. Transform Learning.
All-in-one knowledge management and training platform for your employees and customers.
New to Zoho Recruit?
Zoho Developer Community
New to Zoho LandingPage?
Zoho LandingPage Resources
New to Bigin?
Topic Participants
Shri Rakkshaa Gk
Sticky Posts
Easily perform calculations using dates with the new DATEDIF function
Hey Zoho Writer users! We've enhanced Zoho Writer's formula capabilities with the new DATEDIF function. This allows you to calculate the difference between dates in days, months, and years. Function syntax: =DATEDIF(start_date, end_date, unit) Inputs:Zoho Writer's WordPress extensions
Hey Zoho Writer users! Say goodbye to all your WordPress content publishing woes with Zoho Writer's WordPress extensions. Publish content with all your formatting and images, republish content when you update a document, and more—from a single windowDate-based conditions and filters
Configure conditions with date Hi everyone! We are excited to announce that you can now compare and filter data with date-based conditions. This update lets you compare date fields in a document to a reference date and display a text or value if theIntroducing group by, aggregation, and repeating regions in mail merge templates
Display data exactly the way you want and highlight key insights with Zoho Writer's enhanced merge templates. We've supercharged Zoho Writer's merge templates with the capability to dynamically group, aggregate, and repeat data as blocks. You can nowSay hello to an improved way to merge documents!
Automating all your documents from start to finish is now easier than ever with Writer's new merge tools. If you haven't seen it yet, you can read the main announcement here. Here is the full list of the features we've rolled out: 1. Dynamic Table Headers
New to Zoho TeamInbox?
Zoho TeamInbox Resources
Zoho CRM Plus Resources
Zoho Books Resources
Zoho Subscriptions Resources
Zoho Projects Resources
Zoho Sprints Resources
Qntrl Resources
Zoho Creator Resources
Zoho CRM Resources
Zoho Show Resources
Get Started. Write Away!
Writer is a powerful online word processor, designed for collaborative work.
Zoho CRM コンテンツ
-
オンラインヘルプ
-
Webセミナー
-
機能活用動画
-
よくある質問
-
Ebook
-
-
Zoho Campaigns
- Zoho サービスのWebセミナー
その他のサービス コンテンツ
Nederlandse Hulpbronnen
ご検討中の方
Recent Topics
How to Create a Fixed Sliding Time Window (D-45 to D-15) in Zoho Analytics ?
Hello, I would like to create a report in Zoho Analytics based on a sliding time window between D-45 and D-15, with a fixed snapshot of that specific period. The data displayed should strictly reflect activity recorded between D-45 and D-15 only, withoutHow exactly does "Reply assistance" work in Zoho Desk? What context is sent to the LLM?
Hi, Im trying to better understand the technical behavior of the feature "Reply assistance" in Zoho Desk, and I couldn’t find detailed information in the current documentation. Specifically, I have questions about what data is actually being sent to theHow Does Knowledge Base Search and Article Recommendation Work?
Hello, I would like to understand how the Knowledge Base search engine works. Specifically, does it search based on: The article title only? The full article content? Both, the article and the content? Keywords? Tags? Also, how does the system determineView Answer Bot conversations?
We are trialing Zia and are experimenting with Answer Bot on our knowledge base. So far so good! Management asks me if it is possible to view Answer Bot conversations, the purpose being to look over its shoulder and confirm that it is working as desTrain Zia answer bot on only part of Knowledge Base?
We are trialing Zia answer bot and hope to use it on the knowledge base to help our users find the information they are looking for. I have found how to train Zia on the entirety of our knowledge base. But is there a way to train it on only certain categories🚀 WorkDrive 6.0 (Phase 1): Empowering Teams with Content Intelligence, Automation, Accessibility, and Control
Hello, everyone! WorkDrive continues to evolve from a robust file management solution into an intelligent, secure, and connected content collaboration platform for modern businesses. Our goal remains unchanged: to simplify teamwork, strengthen data security,Zoho Campaigns: An Outstanding Email Marketing Tool
Introducing Zoho Campaigns! A product designed by Zoho, the Zoho Campaigns is made to create, deliver, and manage integrated email campaigns that can help in boosting the sales of a company and its customer base. Zoho Campaigns is actually an email marketingZoho Creator Developer Console | Improved Distribution and Lifecycle Management for apps
Hello everyone, We're excited to introduce new enhancements now in the Zoho Creator Developer Console. These updates strengthen private app distribution through licensing controls and extend environment support across all installed apps, helping teamsAnchor Links in Dashboards
Hello, Our dashboards frequently have multiple sections that would be more easily skipped between using anchor links. Please consider adding an anchor link feature to the text widget? This could be done by adding an anchor link option to the text widget next to the "remove" option (see screenshot). The option would assign an ID to the <div> containing the text widget in the live dashboard. Then, the chosen ID could be linked using a traditional <a href="#link_id"> in the html section of the textZoho CRM for Everyone's NextGen UI Gets an Upgrade
Hello Everyone We've made improvements to Zoho CRM for Everyone's Nextgen UI. These changes are the result of valuable feedback from you where we’ve focused on improving usability, providing wider screen space, and making navigation smoother so everythingSync images with Shopify/Cart
Hello, sync images with shopify or other cart, it cuts out the double work of having to upload to shopify/cart and zoho. ThanksAllow selection of select inactive users in User data fields
Hello, We sometimes need to select a previous employee that has an inactive account in the User data field. For example, when doing database cleanup and indicating actions are done by a certain employee that weren't filled out when they were part of theIs it Possible to Modify Standard Report Urls
Is there a way to permanently modify standard report Urls? Use case: Suppose I have a Products report. Showing list as timeline, calendar, or kanban doesn't make sense. Want to hide that from users by adding #Report:Products?zc_ShowAs=false&zc_Print=falseAssessment Answered - Automation (Related List)
Hello everyone, We have linked a candidate assessment to our job posting. When someone applies, they are required to answer all the assessment questions. However, some candidates submit their applications without completing the questions. In such cases,Smarter holiday planning with yearly-specific Holiday Lists
Hello everyone! Managing holidays and business hours is now easier and more efficient. Holiday Lists now support holidays that fall on different dates every year, while business hours now supports more than one holiday list. This helps businesses manageExternal User onboarding for zoho connect is not really intuitive.
So the external user is sent an invite, which has a button that directs them to login to zoho to view the invite, but if they don't have a zoho account, they cannot access that invite, which seems kinda silly, as there is not real way on for them to createHaving trouble fetching contents of Zoho Connect Feeds using the API, requesting alternative API documentation.
I'm trying to retrieve feed/post data from Zoho Connect using the API but facing challenges with the current documentation. What I've tried: OAuth authentication is working correctly (getting 200 OK responses) Tested multiple endpoints: /pulse/nativeapi/v2/feeds,How to upload file to Connect using API?
Hi there. I looked at the API documentation and nowhere did it mention how to use the API method to upload a file even though it is mentioned that it is possible to be done so. Please help.Select the task view on the board in the Zoho Connect iPhone app
Hello. How do I select the task view on the board in the Zoho Connect iPhone app? The Android app has this functionality.The power of workflows in Zoho Marketing Automation - Video Webinar
In this Zoho Marketing Automation video webinar, our experts walk you through: Why you may want to create marketing workflows How to create marketing workflows Use Zoho CRM data and apply workflows to automate your marketing strategy How workflows canAuto tagging
Some of the articles I enter into Notebook get there when I enter them in Raindrop.io and IFTTT copies the articles in Notebook. When this happens the notes are tagged but instead of useful one word tags with topic the tag pertains to the specific articleConstant refresh required in lots of Zoho tabs
"Hey Zoho, if you can sync my notification bell across 15 tabs using a BroadcastChannel, why can't you send a 'Data Refresh' signal the same way? We don't need a browser reload—we just need the data to sync without us clicking F5 like it's 1999." "PS:What's New in Zoho Billing | January 2026
Excited about the latest enhancements in Zoho Billing? Our January updates bring an intelligent AI assistant, smarter subscription management, and improved tax compliance, saving you time and reducing manual work. Dive into the details below to see howCliq iOS can't see shared screen
Hello, I had this morning a video call with a colleague. She is using Cliq Desktop MacOS and wanted to share her screen with me. I'm on iPad. I noticed, while she shared her screen, I could only see her video, but not the shared screen... Does Cliq iOS is able to display shared screen, or is it somewhere else to be found ? RegardsInserting images into Articles or Knowledgebase
Hi, Are there any plans in improving the Knowledgebase text editor so it would allow inserting images through Windows clipboard via copy-paste? Say for example I took a screenshot using the snipping tool in Windows and I'd like to insert that image toLinks not functioning in Zoho mail
Links that are included in emails I receive are not activating. Nothing at all happens when I click on them. I have researched FAQs and this forum to no avail. Any suggestions?Zoho Mail iOS app update: Manage folders and tags
Hello everyone! In the most recent version of the Zoho Mail iOS app, we have brought in support to manage(create, edit and delete) the folders and tags. Create folders Create Tags Edit/ Delete folder In addition to this, we have also brought in supportZoho Social API for generating draft posts from a third-party app ?
Hello everyone, I hope you are all well. I have a question regarding Zoho Social. I am developing an application that generates social media posts, and I would like to be able to incorporate a feature that allows saving these posts as drafts in Zoho Social.[Important announcement] Zoho Writer will mandate DKIM configuration for automation users
Hi all, Effective Dec. 31, 2024, configuring DKIM for From addresses will be mandatory to send emails via Zoho Writer. DKIM configuration allows recipient email servers to identify your emails as valid and not spam. Emails sent from domains without DKIMCreate an Eye-Catching Announcement Widget for Your Help Center
Hello Everyone! In this week’s edition, let’s explore how to keep your customers updated with exciting news in the Help Center. See how ZylkerMobile wowed their customers by bringing updates right to their portal. ZylkerMobile, the renowned brand forUI issue with Organize Tabs
When looking at the organize Tabs window (bellow) you can see that some tabs are grayed out. there is also a "Add Module/Web Tab" button. When looking at this screen it's clear that the grayed out tabs can not be removed from the portal user's screenSuper Admin Logging in as another User
How can a Super Admin login as another user. For example, I have a sales rep that is having issues with their Accounts and I want to view their Zoho Account with out having to do a GTM and sharing screens. Moderation Update (8th Aug 2025): We are workingTask list flag Internal/External for all phases
Phases are commonly used in projects to note milestones in the progression of a project, while task lists can be used to group different types of tasks together. It makes sense to be able to define a task list as either internal or external however theZoho CRM Feature Requests - SMS and Emails to Custom Modules & Time Zone Form Field
TLDR: Add Date/Time/Timezone form field, and be able to turn off auto timezone feature. Allow for Zoho Voices CRM SMS Extension to be able to be added to custom modules, and cases. Create a feature that tracks emails by tracking the email chain, ratherOur Review Of Zoho CRM after 60 Days
The purpose of this is to just share with Zoho why I love their product, but ultimately why I could not choose Zoho CRM for our next CRM. About two months ago we begun a CRM exploration process for our financial planning firm, based in Texas. We alreadyLink Purchase Order to Deal
Zoho Books directly syncs with contacts, vendors and products in Zoho CRM including field mapping. Is there any way to associate vendor purchase orders with deals, so that we can calculate our profit margin for each deal with connected sales invoicesExtend the Image Choice Field
Hi, The New Yes/No field is great for what it does, and the Image Choice Field is good but could be better with some functions from the Yes/No field. Take an example, rather than just Yes/No you want Yes/No/Maybe (Or more than 3 choices), but unlike theCRM x WorkDrive: File storage for new CRM signups is now powered by WorkDrive
Availability Editions: All DCs: All Release plan: Released for new signups in all DCs. It will be enabled for existing users in a phased manner in the upcoming months. Help documentation: Documents in Zoho CRM Manage folders in Documents tab Manage filesNew 2026 Application Themes
Love the new themes - shame you can't get a little more granular with the colours, ie 3 different colours so one for the dropdown menu background. Also, I did have our logo above the application name but it appears you can't change logo placement positionZoho Desk: Macro to assign Ticket to self
Hello, We are using macros in Zoho Desk to set some fields and send a response. I would also like to assign the ticket to myself (or whoever applies the macro). I can only set a fixed agent in the macro, so I would have to create one for every agent.Next Page












