Zoho Creator | Introducing Augmented Reality
We're delighted to announce augmented reality (AR) in Zoho Creator! Now, you can set up your own immersive 3D experiences—combining a glimpse of the real world with computer-generated graphics. AR technology augments what you see, by superimposing digital data (3D models) on real-life objects, captured by your device camera. This real-time digital interaction provides better data visualization and enhances end-user experiences, providing you with exciting new business opportunities.
AR is seamlessly accessible via web browsers, smartphones, and tablets, which facilitates the growing interest in multi-experience development platforms (MXDPs). Using AR, your businesses can provide unique approaches to key business challenges in real-world applications.
AR can enhance user experience in many ways:
Organizations can use AR to promote their products or services and launch innovative marketing campaigns.
A rich feedback loop can be created using AR in product customization and quality, where users can select the defective products and also annotate the 3D models by describing the defects.
Users can try out different products virtually, check if a product fits well in their rooms (in the case of furniture products) by either partial or full replacement of the original view of a product with an augmented view of the same product, and make informed choices, all within the comfort of their homes.
AR types in Creator
Marker-based AR: This AR-type relies on the recognition of images (referred to as markers). Markers are unique, visual patterns that your device cameras can easily recognize and process. For example, you can point your devices at markers such as scan codes or logos to seamlessly activate the AR experience. Marker-based AR works by scanning a marker, which triggers the content to be overlaid on the camera upon visuals matching the marker image For example, students can scan a diagram in their textbook and view its 3D model (projected on the diagram) through their digital devices.
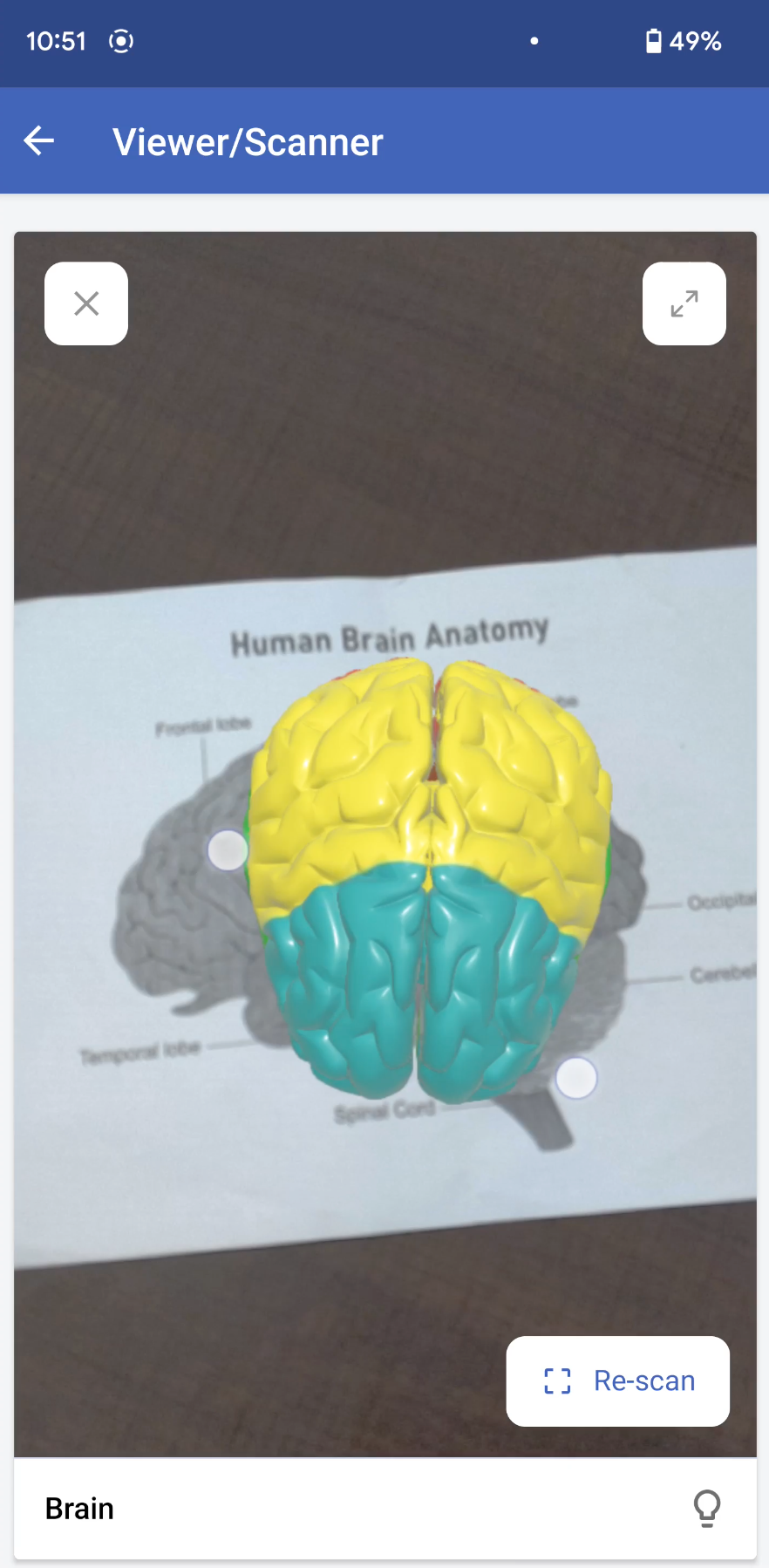
Markerless AR: This AR type does not use a marker. Instead, it allows you to scan the real environment and place digital elements on the recognized (flat) surface. This offers more control to users, as it allows them to choose where they would like to place the virtual object (including real-life placement of virtual augmented objects). For example, furniture companies can enable customers to virtually place their furniture in their homes to check if it would fit well.
In the markerless AR type, users can preview the models in the following two modes:
AR mode: This mode displays the 3D model as superimposed on its environment. Users can rotate/move their devices to view the plotted model.
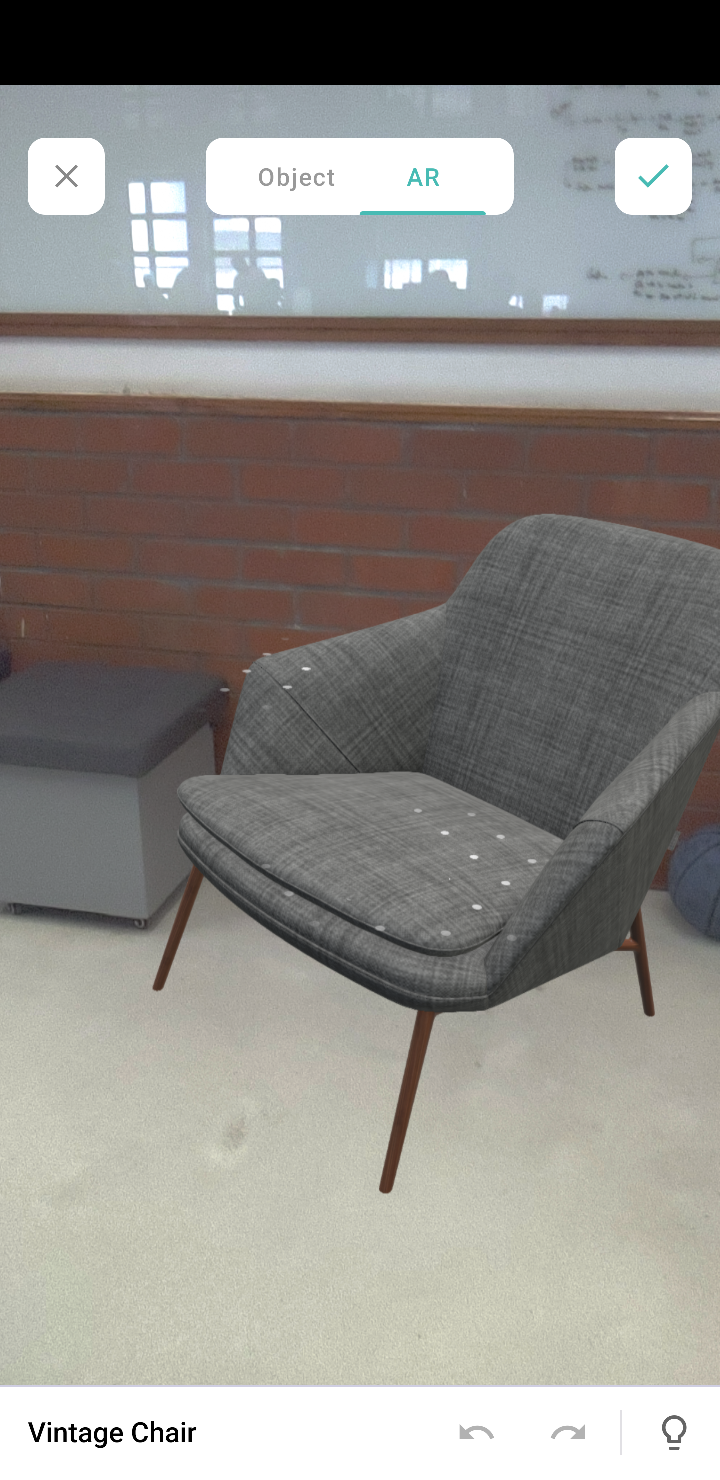

Object mode: This mode displays only the 3D model. It allows you to view the selected/scanned model in a 360˚ rotation. You can also zoom in and zoom out the model, as per your convenience.
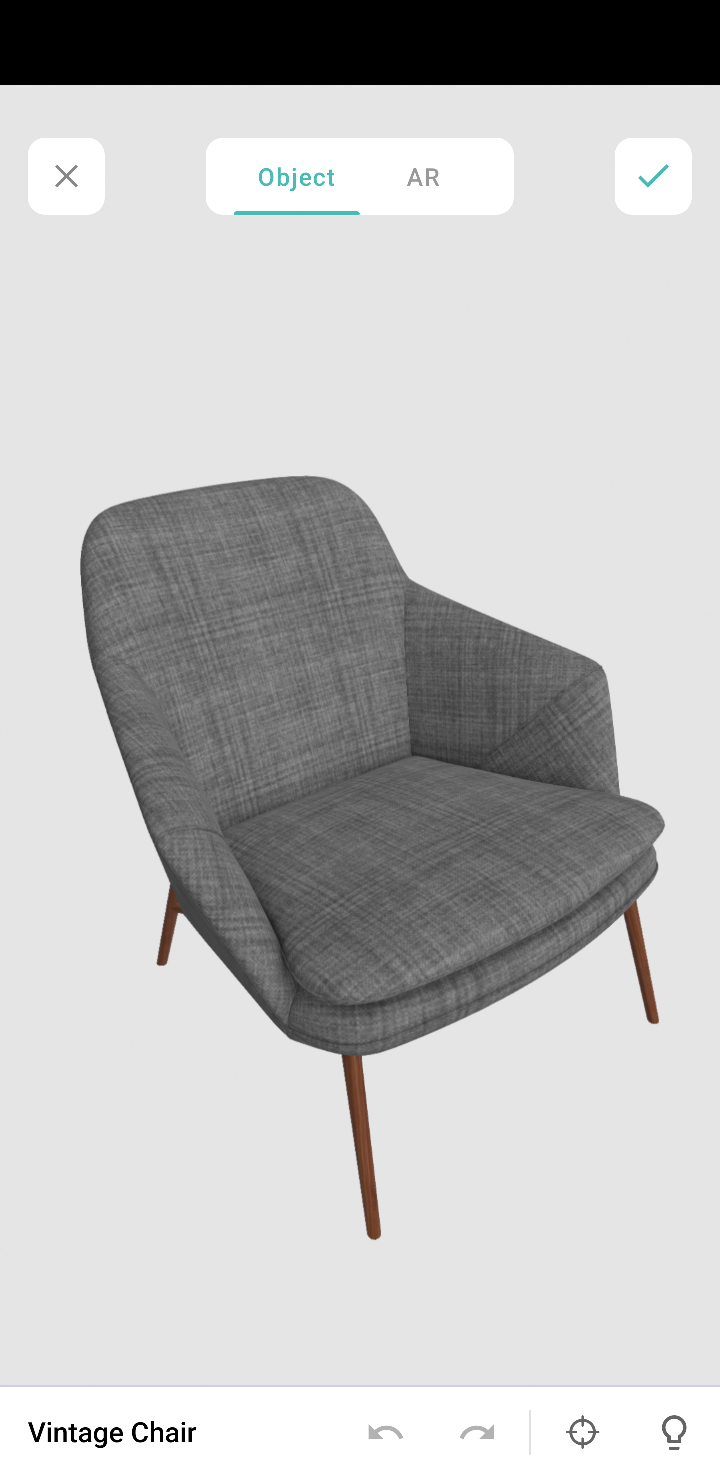

Note: These modes are available in the AR field and AR viewer (only for markerless inputs).
AR in Creator
In Creator, AR has been introduced across three modules:
Microservices - AR Library
Form fields - AR field
Pages - AR Viewer
AR Library
AR library stores AR sets of all the apps in your Creator account. You can add and manage AR sets from here. An AR set consists of AR elements such as 3D models and their markers.
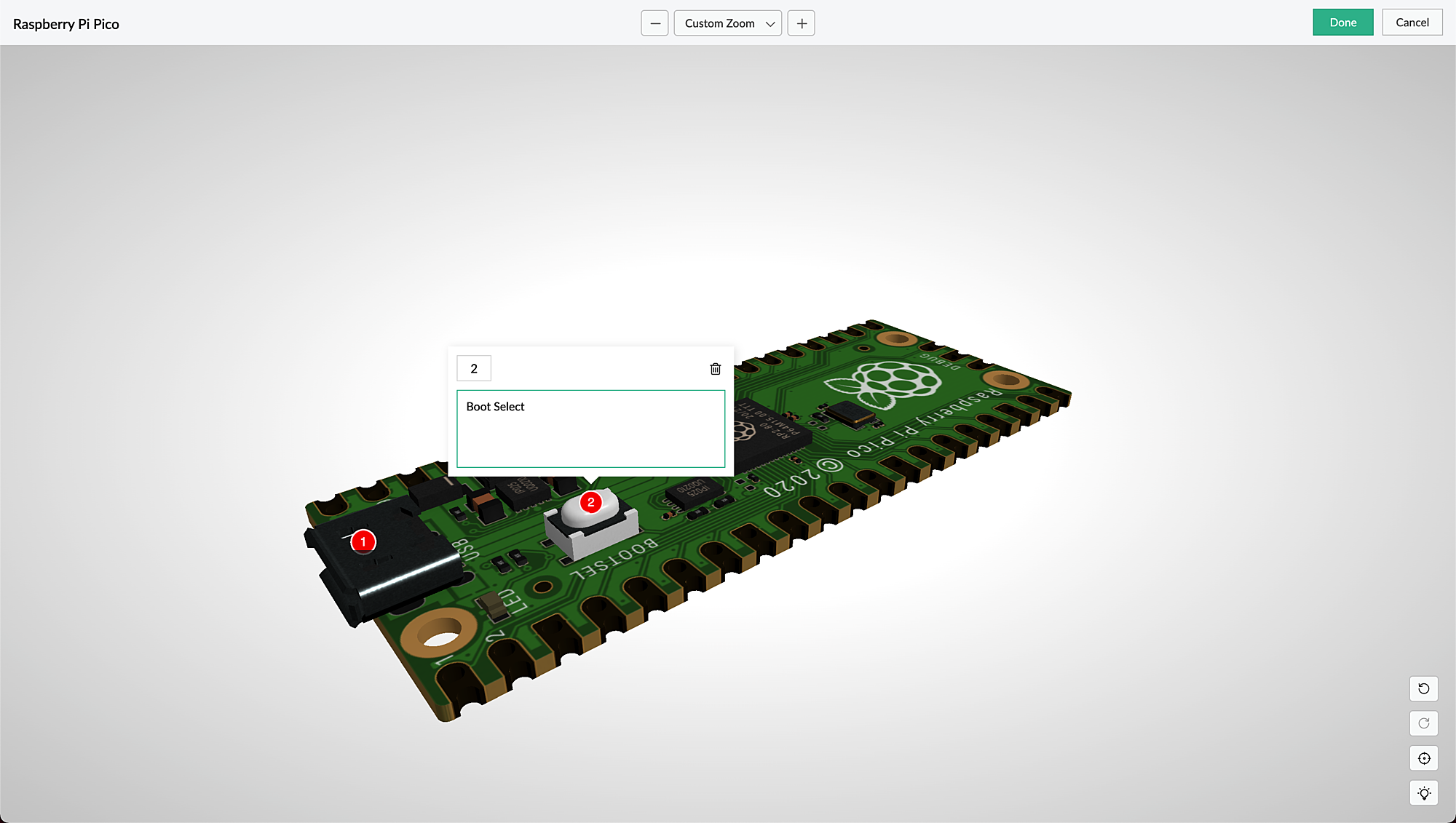
AR field
The AR field in a form displays the AR sets (3D models) from the AR library as a dropdown. You can add the AR sets in the AR Inputs field property. When you access your app in live, you can choose a model from either marker-based or markerless AR sets, and you can annotate it.
AR Viewer
The AR Viewer acts as an interface for your device's camera. This interface is used to invoke the camera (only in mobile) to scan a marker for your marker-based AR sets. In your app's page, you can configure the AR Viewer's input in two ways:
Marker-based AR Sets: To scan the marker and plot the respective 3D model.
Passing the 3D model's name through page parameters to load a 3D model directly.
Illustration
1. Imagine you've created an app named Zylker Jewelry. The following flowchart shows how AR is used across this app.
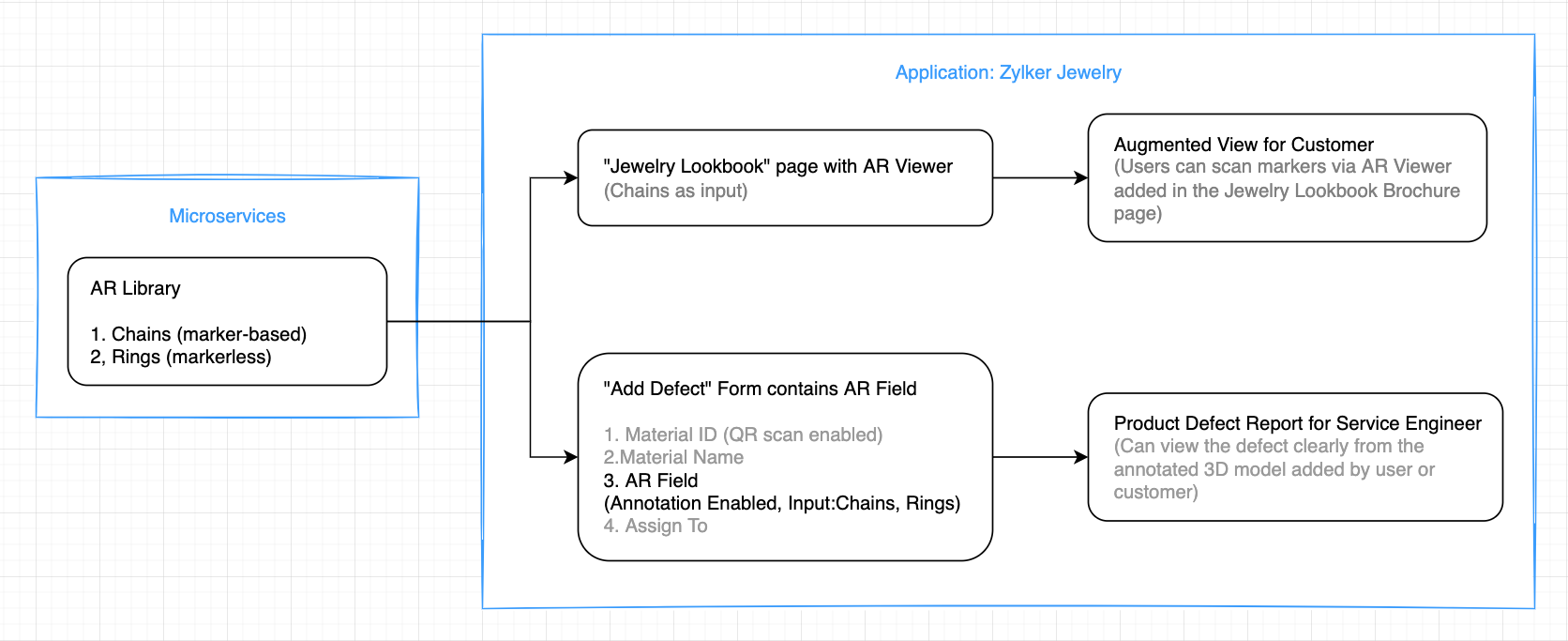
This app enables you to perform the following actions:
(i) Users can use the scanner (AR viewer) on the app's Jewelry Lookbook page to scan the various designs available on your brochure and view them as popup models. They can rotate, zoom in and zoom out, and view the models in full-screen as well.
(ii) Quality assurance engineers can select 3D models of the defective jewels and also annotate them by describing the defects.
Let's take a look at how the above actions can be configured in the Zylker Jewelry app.
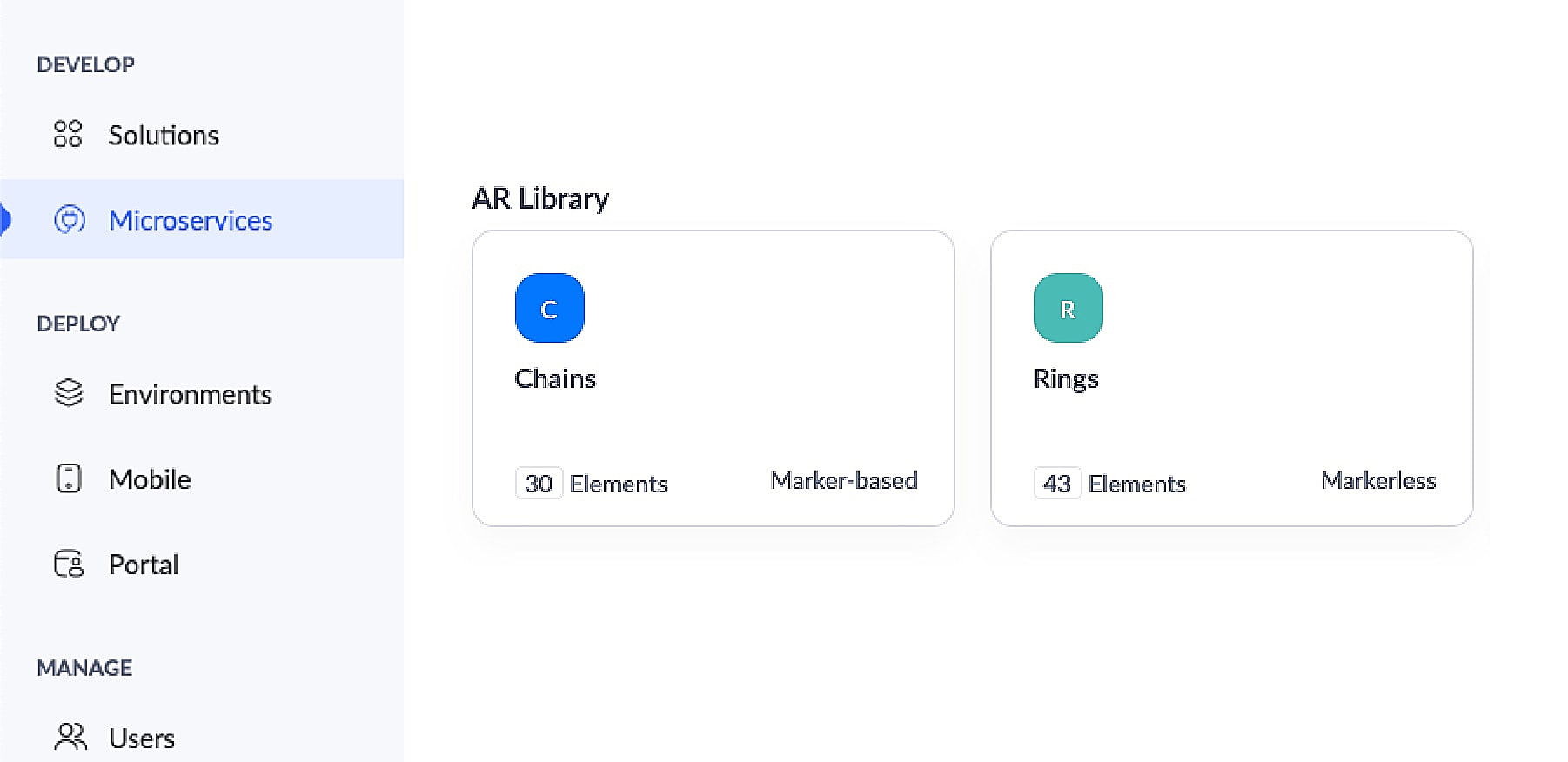
This app has an AR library that contains 3D models of chains (marker-based) and rings (markerless).
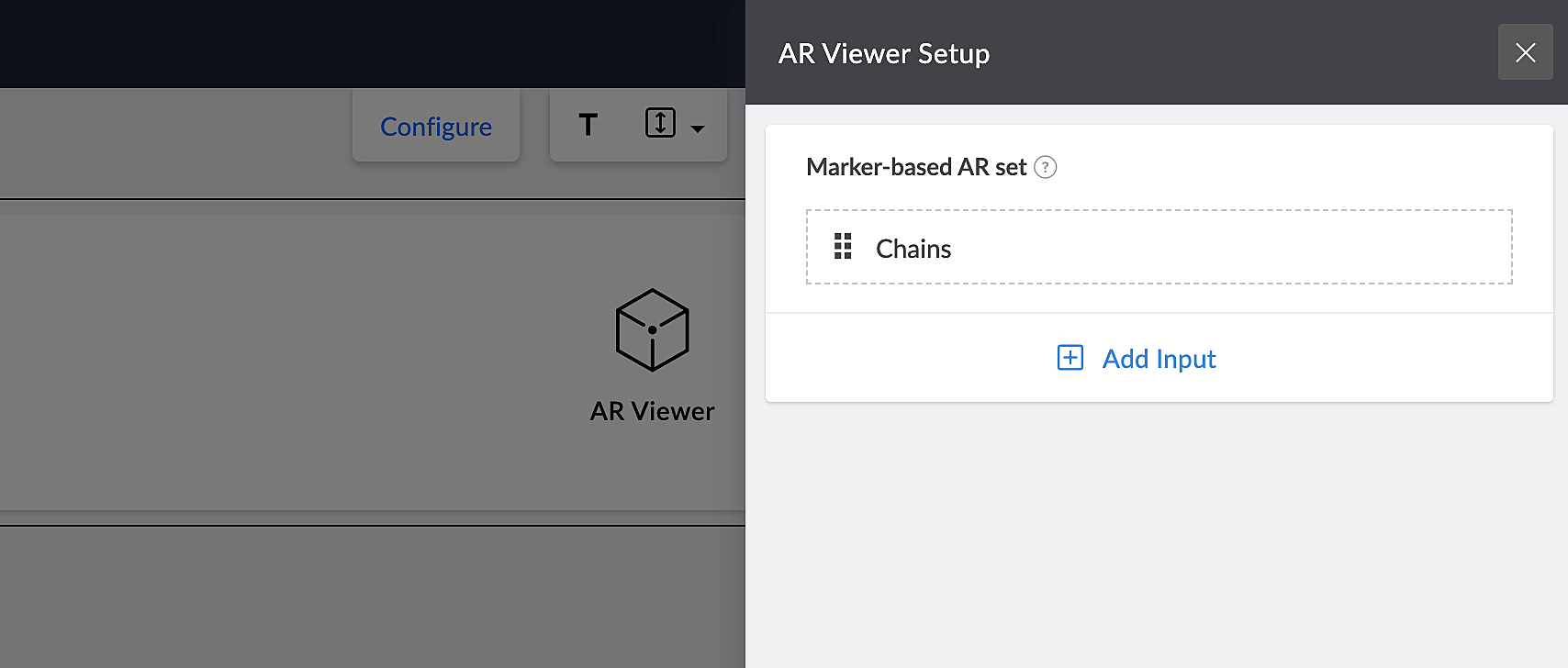
The app's Jewelry Lookbook page has an AR Viewer element with the 3D models of chains as its input. When users access this page, they'll be able to scan the brochure and view the available chain designs on their devices.
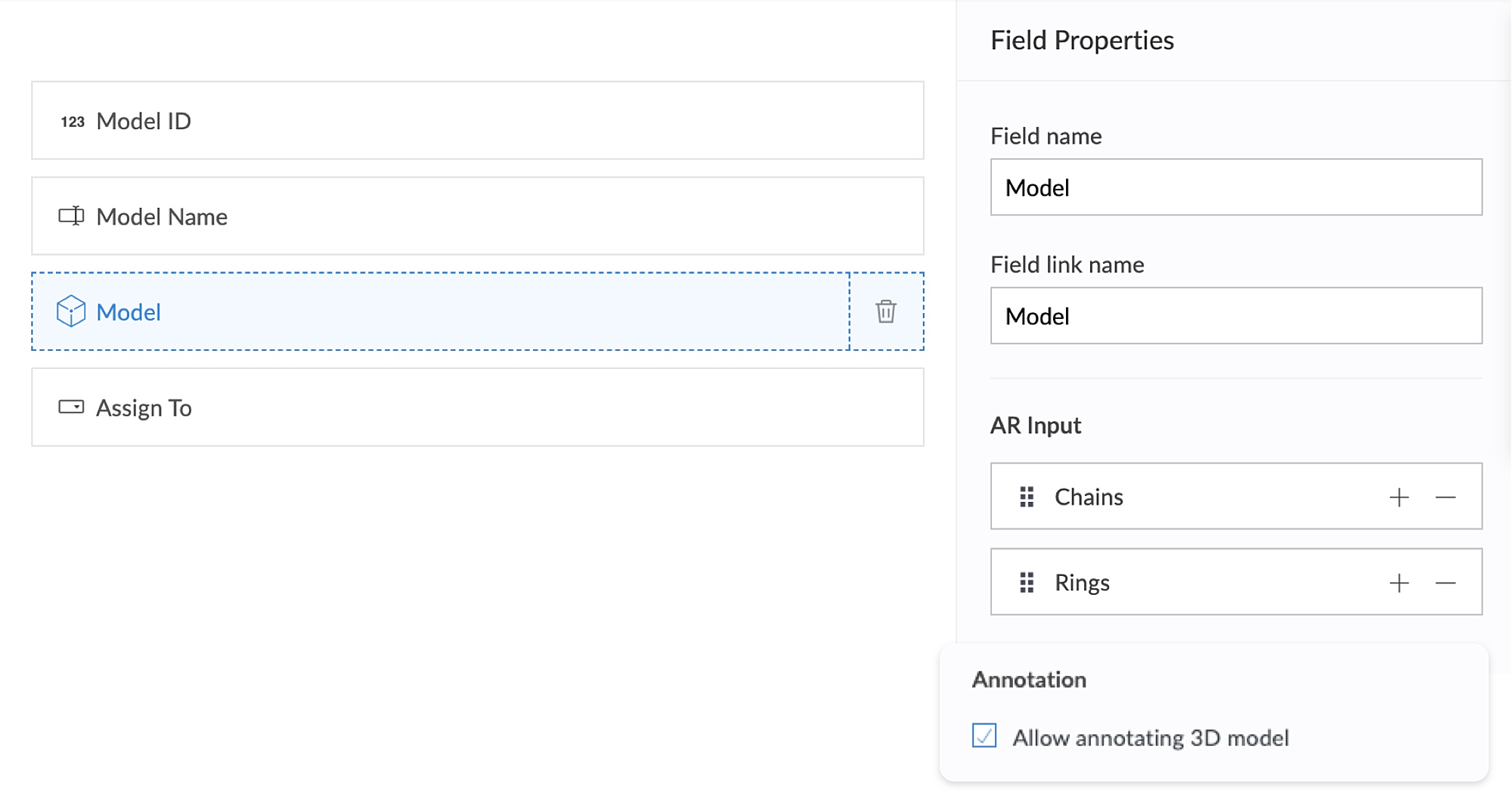
The app's Add Defect form has an AR field containing the 3D models of chains and rings as its AR input. Quality assurance engineers can select the 3D models of defective jewelry from the dropdown and annotate the models by describing the defects. This form also has an Assign To field, that assigns the defect to the designated Service engineer, who can view and take appropriate action.
2. Using AR, classroom education can become all the more intuitive and interactive, as it enables teaching staff to demonstrate virtual examples of textbook concepts. This, in turn, will enable students to engage more actively, learn faster, and memorize information more easily.
Let's take a look at Zylker Schools of Learning, a learning app created for teachers and students. This app facilitates interactive learning through AR technology used across the following components. Apart from these, AR functionality can also be accessed via your mobile applications.
AR Viewer
AR field
AR Viewer:
This app has an AR library that contains textbook diagrams as markers, along with their 3D models. The app's Virtual Book page has an AR Viewer element with the 3D models as its input.
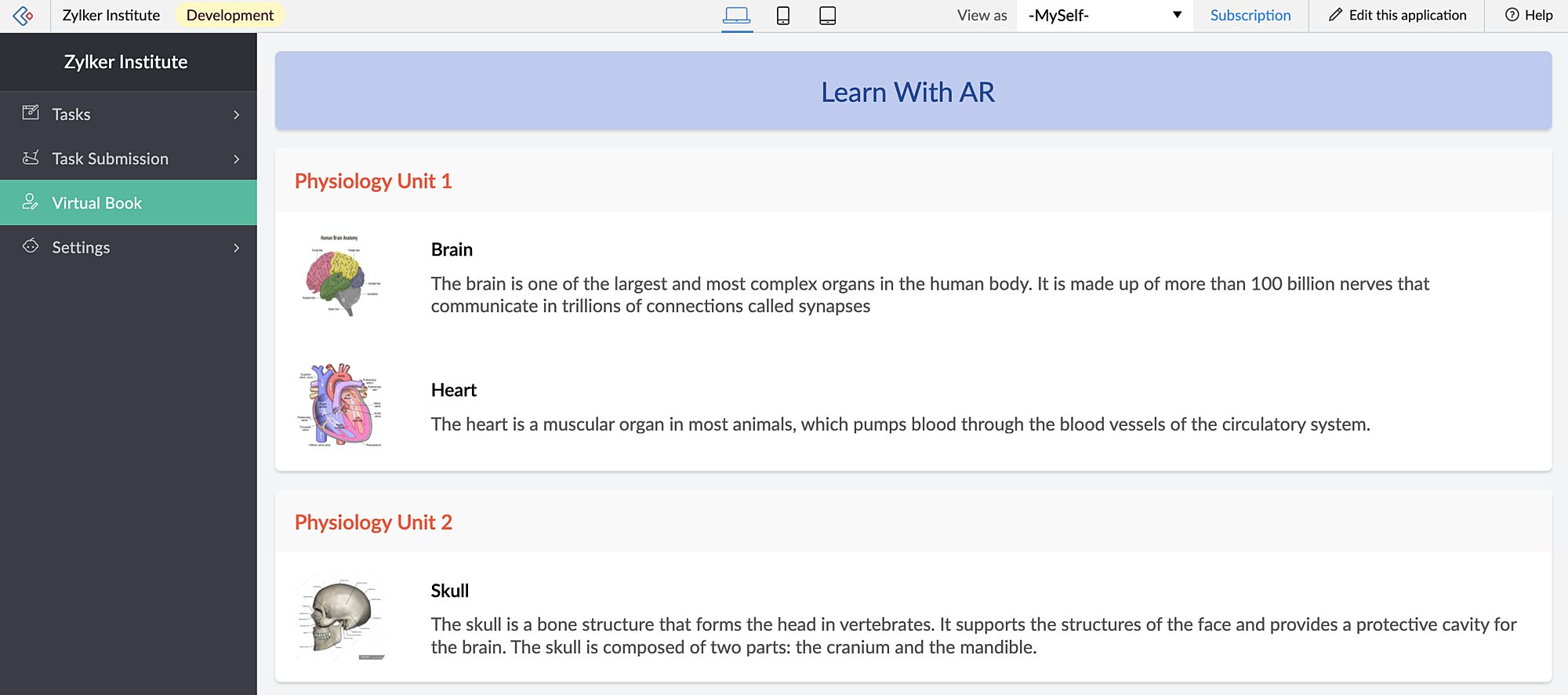
When students access this page, they can click the diagrams and view them in both AR mode and Object mode — rotate, zoom in and zoom out and view in full-screen as well.
When you access the app via mobile, apart from viewing the diagrams in AR Viewer (similar to web), students can also open their device scanner, scan their textbook diagrams and view them as plotted (popup) models on top of their textbook.
AR field:
This app has a New Task form that contains an AR field. This field has 3D diagrams as its input. You can assign tasks to your students, asking them to annotate the 3D models and also view the submitted tasks.
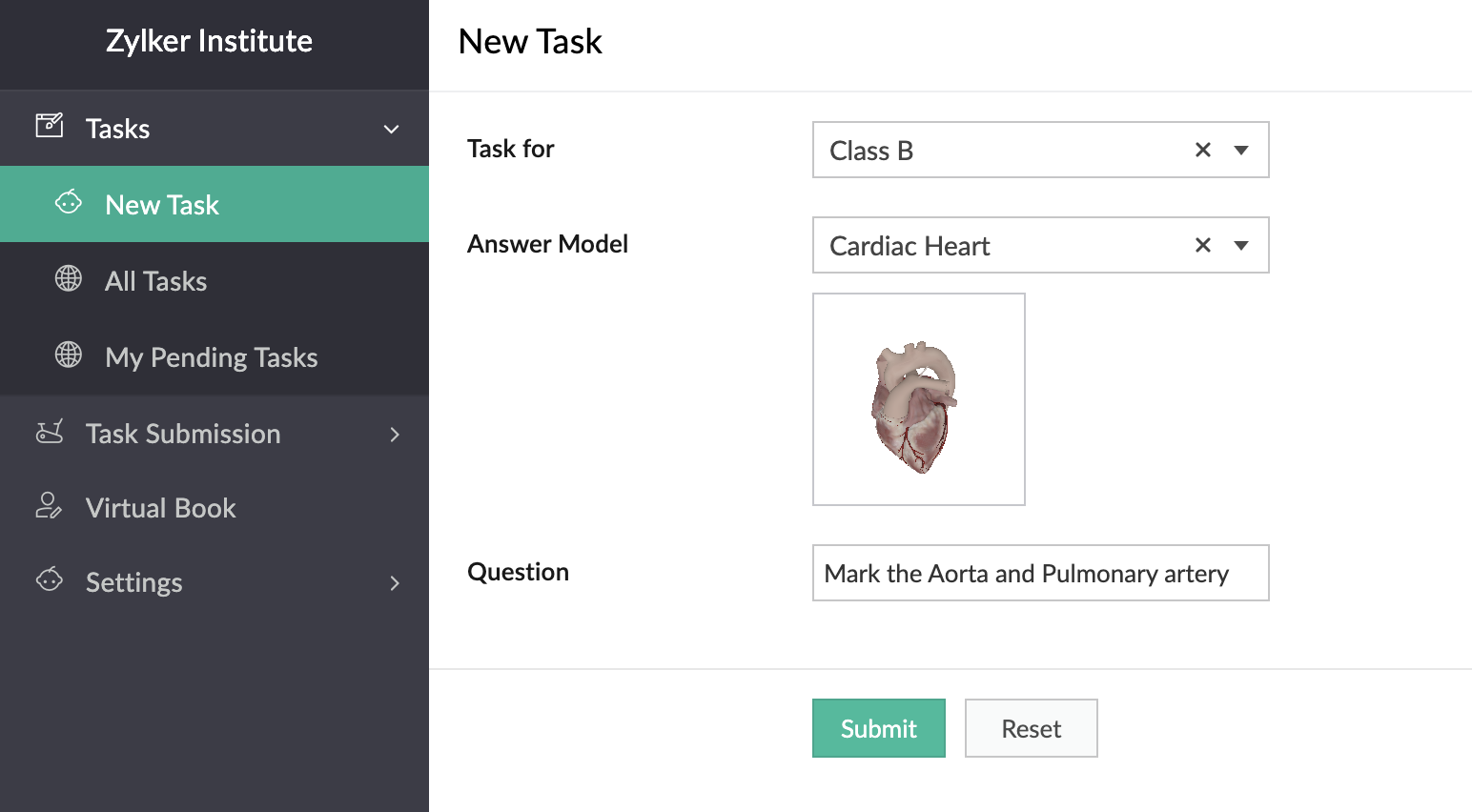
In the below GIF, the demo user Demo 3 is the Teacher profile and Demo 1 is the student profile.
You can also place stickers of the textbook diagrams on your classroom walls, which can be scanned by your students through the provided devices. Upon scanning the sticker, they can view, rotate, and annotate the 3D model of the scanned image which is mapped in the AR Library.
Thus, AR helps in explaining otherwise plain textbook concepts in a visually-appealing manner.
Feature release plan
AR in Creator will be available in C6 for Paid plan users only.
If you have any questions related to AR, please feel free to contact us at support@zohocreator.com.
Regards,
The Zoho Creator Team
All-in-one knowledge management and training platform for your employees and customers.
Zoho Developer Community
Topic Participants
Meghaa Pradyumnan
Catherine
Damien Cregan
PARTHIBAN VALLAVAN
Sriram U
Sticky Posts
Introducing Zoho Creator's 2025 Release Projection 2
Hello Creators! I'm Prakash, from the Creator product management team, and today I'm delighted to unveil our next set of features as part of Release Projection 2 for 2025. With thoughtful analysis and planning, we've curated powerful new capabilitiesZoho Creator - 2023 Release Projection 1
Hello everyone! A very Happy New Year to you and your family. Hope you're all good and having a great time using Zoho Creator to make your lives easier and your businesses prosper. 2022 was an action-packed year for us at Creator, and we hope to continueZoho Creator User Group meetups in a city near you! - Oct - Nov, 2023
Greetings from the Zoho Creator team! We're hosting a series of Zoho Creator meetups in various cities across the globe, and we'd love to meet you there! Our meetups are a great opportunity to network with industry peers, exchange ideas and best practices,Zoho Creator - 2023 Release Projection 2
Hello everyone! Time truly flies when you're having an incredible journey, and today we mark the completion of an eventful and action-packed six months. It feels like just yesterday when we embarked on this adventure together with the launch of our newUpcoming Updates - August 2022
Hi all, Greetings from the Zoho Creator team! Today we've got news for you on some exciting updates. And rest assured— there’s more to come! In this post, we'll be going over the upcoming features and improvements for this month as mentioned below. A
Zoho TeamInbox Resources
Zoho CRM Plus Resources
Zoho Books Resources
Zoho Subscriptions Resources
Zoho Projects Resources
Zoho Sprints Resources
Qntrl Resources
Zoho Creator Resources
Zoho CRM Resources
Zoho Show Resources
Get Started. Write Away!
Writer is a powerful online word processor, designed for collaborative work.
-
オンラインヘルプ
-
Webセミナー
-
機能活用動画
-
よくある質問
-
Ebook
-
-
Zoho Campaigns
- Zoho サービスのWebセミナー
その他のサービス コンテンツ
Nederlandse Hulpbronnen
ご検討中の方
Recent Topics
Project Notifcatiion Emails - Milestone
Hello: I cannot get myself, or most importantly my portal client user to recieve an email upon completion of a milestone. I have set up our 1st project. I have set up a test client user. (accepted the invitation and is listed in the system as a clientZoho Forms - Feature Request - Year Field
Hi Zoho Forms Team, You currently have the following date and time fields: Date Time Date and Time Year and Month It would be useful if you could include a "Year" field For example a recent application I completed said "What year was your house built?"Integrate Excel or Zoho Sheet functions / calculations to CRM product module
Hello Community, I hope someone more experienced can help me with this question. Our price / payment plan calculations are in an Excel spreadsheet and I would like to use all those functions / calculations in my Products module. So when we send a quoteSync CRM Contacts to USER'S contacts on Office 365
I can see that the O365 sync is transferring contacts backwards and forwards between Zoho CRM and Office365. But it has created a separate address book in Office 365 called "Zoho CRM Contacts". This address book is not used by Office/Outlook's email functionHow can I link Products in a Deal Subform to the Products Module
Hello, I have a pricing subform on our Deals page and use a lookup field to associate a product with each line. I want to be able to look at a product page within the Products module and see a list of the deals connected to that product. I have this workingManage Every Customer Conversation from Every Channel inside Zoho SalesIQ
Your customers message you from everywhere. But are you really able to track, manage, and follow through on every conversation, without missing anything? With interactions coming in from websites, mobile apps, and messaging platforms like WhatsApp andZoho Books | Product updates | February 2026
Hello users, We’ve rolled out new features and enhancements in Zoho Books. From Advanced Reporting Tags to the ability to mark projects as completed, explore the latest updates designed to improve your bookkeeping experience. Introducing Advanced ReportingUpdate latitude & longitude address field API
How do I update the coordinates of an address field from a widget? I can't modify the latitude and longitude of the address field. I think the problem is how I'm writing formdata variable. zoho_init.then(function (data) { var queryParams = ZOHO.CREATOR.UTIL.getQueryParams();Zoho Forms - Feature Request - Past Into Scanning/OCR Field
Hi Zoho Forms Team, You recently introduced the OCR/Scanning field which I have found great use for with one client who receives work orders as a screenshot from one customer. I want to raise a feature request here which would make that field even moreinability to use different primary address on invoice per location
my company operates in two different locations with different email address. The problems then is the inability to edit the primary to suite the invoice for the second location.Zoho Books - Breaking A Working App
We've been using Zoho for many years now. Across all apps, entering phone numbers in standard formats was enabled in all apps. These formats are: xxx.yyy.zzzz xxx-yyy-zzzz (xxx) yyy-zzzz and we were able also to add extension numbers in these formats:No Need To Fix Something That Is Working
Zoho Books is a great financial tool which helps businesses to become more efficient and productive with day-to-day operations. As such, every change, upgrade, improvement needs to be carefully thought before implemented in the software and I'm sure ZohoUse Zoho Creator as a source for merge templates in Zoho Writer
Hello all! We're excited to share that we've enhanced Zoho Creator's integration with Zoho Writer to make this combination even more powerful. You can now use Zoho Creator as a data source for mail merge templates in Zoho Writer. Making more data fromAnyone in Australia using Zoho Books AND has their account with NAB?
Hi I have an account with both NAB and Suncorp. Suncorp transaction come in the next day however NAB transactions take 4-5 business days to appear. eg: A deposit made today in my Suncorp will be imported into Zoho tomorrow. A deposit made today to the NAB account will be imported maybe Saturday (Friday overnight). I have contacted both Zoho and NAB but noone seems to know why. I was just wondering if anyone else in Australia uses NAB and has this issue (or doesn't) maybe we could compare notes andDetailed Balance Sheet for tax preparer
I'm using the free edition of Zoho Books. My tax preparer is asking for "detailed" Profit & Loss and Balance Sheet reports which include all the activity and transactions within the various categories. The default reports do not include these details.On Edit Validation Blueprint
Hello, I have a notes field and a signature field. When the Approve button is clicked, the Signature field will appear and must be filled in. When the Reject button is clicked, the Notes field will appear and must be filled in. Question: Blueprint willZoho Projects - Cloning a task does not trigger task workflow when created
Hello! I have a Project where my team uses a set of tasks from a tasklist as templates, so we could simply clone it and drag it to another list in kanban view to avoid creating a new one from scratch. The process works well, but after cloning it the newHost Group Appointments Online in Zoho Bookings
Greetings from the Zoho Bookings team! We’re excited to announce a new enhancement to Group Booking that makes hosting online group events smoother and more professional than ever. You can now conduct online group events with auto-generated meeting linksCan't rename groups on Mac desktop app
I'm working on an up-to-date Mac with a freshly downloaded Notebook app. I'm trying to rename a group within a notebook. Here I have, left to right, a note, a group, and a note. I select the group. On the top left, I select Action. On the dropdown, "Rename"Workdrive Collaboration with an External User
I would like to know if I can setup a collaboration space with an external user in workdrive or do I need to add them as a user on my system? If I need to add them, can I add them on Workdrive only and give limit access to our space only?Delete button
Hi, The delete button were hide into the three dot button. Can I display outside? why Zoho make this update?FSM integration with Books
Hi, I have spent a few months working with FSM and have come across a critical gap in the functionality, which I find almost shocking....either that, or I am an idiot. The lack of bi-directional sync between Books and FSM on Sales Orders/ Work OrdersMarketing Tip #23: Help customers with how-to guides and usage tips
Customers don’t stop needing you after they place an order. Helping customers use your product correctly and confidently can improve satisfaction, reduce returns, and increase repeat purchases. Sharing simple how-to guides, usage tips, or care instructionsPowering Customer Support with our women
In Zoho Desk support, women make up 50% of our team. We see this as one of our strengths, reflecting the spirit of this year’s theme, "Give to Gain". Our women find their balance Women carry many responsibilities — they represent frontline support, leadFunction #25: Automatically generate purchase orders from a sales order
We kicked off the "Function Fridays" series with the goal of helping you automate your everyday accounting tasks. As we delve into today's post, I'm delighted to announce that we're here to present the 25th custom function in this series. While it isLooking for Guidance on Building a Zoho Website
I'm exploring the possibility of building a custom website with specific features using Zoho as an alternative platform. My goal is to create something similar to https://gtasandresapk.com , with the same kind of functionality and user experience. I'dAuto-publish job openings on my Zoho Recruit Careers Website
I have developed a script using the Zoho Recruit API that successfully inserts new jobOpening records to my Zoho Recruit website, but my goal is to auto-publish to the Careers Website. The jobOpening field data shows two possible candidates to make thisZOHO Reports are taking longer time to get refresh
Hi Team, Since last few days, I'm facing issues in getting updated reports. For eg: right after making an expense entry or even posting a journal, it is taking longer then expected for the updated reports. Refer below: "You are viewing the report thatInvalid scope choice: Workdrive integration in CRM
Bug: There is an invalid option in the permission choices for Workdrive integration in CRM. If the entry "WorkDrive.teamfolder.CREATE" is selected, it will return a message indicating invalid OAuth scope scope does not exist.Sales IQ chat is not working in signed android apk
I have integrated ZOHO sales IQ support chat and i have followed each step and its working fine in my development build but when i create signed APK for it. Chat does not work in it and showing awaiting for detail. I previously asked the same query butHow to add line breaks in zoho.cliq.postToUser(...) message?
In a CRM function using Deluge I'm sending this message and attempting to add some line breaks but they are ignored. Is there another way to add these breaks? My message: message: New urgent task\nDescription \nThis is a fake description.\n A new line?Enable Free External Collaboration on Notecards in Zoho Notebook
Hi Zoho Notebook Team, I would like to suggest a feature enhancement regarding external collaboration in Zoho Notebook. Currently, we can share notes with external users, and they are able to view the content without any issue. However, when these externalProblem with CRM Connection not Refreshing Token
I've setup a connection with Zoom in the CRM. I'm using this connection to automate some registrations, so my team doesn't have to manually create them in both the CRM and Zoom. Connection works great in my function until the token expires. It does not refresh and I have to manually revoke the connection and connect it again. I've chatted with Zoho about this and after emailing me that it couldn't be done I asked for specifics on why and they responded. "The connection is CRM is not a feature toUpdate Existing Records greyed out in Free Version
Trying to update records from an Excel sheet, and not getting the option to update. Only option is to add as new accounts. All documentation I can see says update should be an option! Accounts, Leads, Contacts, all the same.In Lesson Video
Can anyone help me with this? I'm not sure what happened. It suddenly became like that. I tried to reupload. I tried create a new lesson. Still the same. Please help!emailing estimates
Shows up in the customer mail logs as sent but nobody is receiving them, even when I send them to myself I don't get them ??? Something wrong with the mail server or my end ?Help with deluge script
Hi Community, this is my first Deluge script. I've pieced it together from reading various articles I want to use it in a workflow to 1 Convert a lead to a contact 2. Create a record in a custom module Below is what I have got so far but it does not fireHow to use OR when filtering using two fields
I want to create return a list of Account Names by filtering on Field1 = "yes" OR Field 2 = "no" I can't see how to use the OR in the filter.Mobile phone version not working well
I am working on the Zoho Site Builder. In the preview the desktop version looks okay, but in the mobile phone preview many words are cut off in the weirdest (wrong) way. How can I fix that?Zoho - Please explain difference between Thread view and Conversation view on Ticket
I have reviewed the help document here but am still not clear on the difference between the two views. As an example, I just had a back and forth on a ticket: - Customer emails support email. - I email back from Desk. - Customer responds back. - I email back from Desk. On the upper left drop down box on the ticket Zoho Desk now says this is "4 Threads" and "4 Conversations" . How is that 4 threads?? By my count it is 1 thread and 4 conversations (assuming by "conversation" Zoho means number of totalNext Page












