Customer Segmentation using RFM Analysis
How well do you know your customers? Whether you operate in a B2B or B2C space, chances are that 80% of your business comes from just 20% of your customers (Pareto's Principle). According to a study by Forbes, acquiring new customers costs five times more than retaining the existing ones. Identifying high-value customers is crucial to increase revenue and building brand loyalty.
Customer Segmentation is a critical strategy for businesses to understand and engage with customers effectively. Understanding the behavioral patterns of customers can help personalize the purchases they make and cater to their needs better.
Questions like who are the customers who contribute more to sales, who are the customers about to churn, will help digital marketers understand the behavioral patterns of their customers.
While there are many criteria based on which the customer base can be segmented, this solution focuses on segmenting customers based on the RFM analysis.
What is RFM Analysis?
RFM analysis (Recency, Frequency and Monetary) is a method used to identify and segment existing customers based on their purchasing behavior. The key metrics of RFM analysis include
Recency
Recency refers to how recently a customer has made their purchase and this is the most important metric of the other metrics. This metric is a strong indicator of customer loyalty and interest.
Frequency
Frequency refers to how often a customer makes purchases or interacts with a business within a specific period. It measures the level of engagement and loyalty of a customer.
Monetary
Monetary value refers to the total amount of money a customer has spent with a business during a specific period.
Industry-Specific Applications of RFM Analysis
- SaaS and subscription services: RFM analysis can be adapted for SaaS and subscription services to segment users based on engagement, renewals, and revenue contribution.
- Financial Sector: RFM analysis can improve credit scoring and risk assessment by evaluating customer transaction patterns, helping financial institutions make more informed loan approval decisions.
Data Requirements
For RFM analysis, you'll need a transactional dataset with the following equivalent columns (details)
- A product (Product ID)
- A related transaction (Transaction ID)
- Number of products purchased in a transaction (Product Quantity)
- The product purchase price (Product Price)
- Transaction date (Date)
- Customer who made the purchase (Customer ID, Customer Name)
We have used a sample table of e-commerce data for illustration.
Steps for Implementing RFM analysis
1. Gather and Prepare Transaction Data :
Gather all transaction data, ensuring it includes customer identifiers, transaction dates, and monetary amounts, and address missing or inconsistent values, ensuring data integrity before analysis.
2. Compute RFM Metrics:
To segment customers based on their behavior, we compute three key metrics: Recency (R), Frequency (F), and Monetary Value (M). Below are SQL queries for each, along with detailed explanations.
Recency (R)
Recency measures how recently a customer made a purchase. It is calculated as the number of days since their last transaction. Customers with recent purchases are more engaged, while those who haven’t bought in a long time may be at risk of churn.
The time frame for RFM analysis should be tailored to your business model and industry. Choosing the right period for RFM analysis is essential, as it directly influences the accuracy of customer segmentation and the quality of insights derived.
Frequency (F)
Frequency tracks how often a customer makes purchases within a specific period. A higher frequency indicates a loyal customer who regularly shops, while a lower frequency suggests occasional or one-time buyers.
Monetary Value (M)
The total amount spent by the customer in the same period
RFM Query Table
|
SELECT
"Customer ID",
"Customer Name",
DAYS_BETWEEN(MAX("Transaction Date"), CURRENT_DATE()) AS "Recency",
COUNT ("Order ID") AS "Frequency",
SUM("Transaction Amount") AS "Monetary Value"
FROM "Customer Data"
GROUP BY "Customer ID",
"Customer Name"
ORDER BY "Recency" ASC,
"Frequency" DESC,
"Monetary Value" DESC
|
3. Segment Customers using Cluster Analysis
Manual scoring can skew the results and may not be practical for handling large volumes of data. In contrast, using machine learning algorithms like cluster analysis ensures unbiased, efficient, and data-driven segmentation. Unlike traditional scoring methods such as the quantile or percentile-based approach, cluster analysis recognizes inherent relationships and patterns in the data. With cluster analysis, business can obtain accurate segmentation and devise targeted strategies to improve sales and customer retention.
Follow the below steps to apply cluster analysis,
- Click the Create New icon and choose New chart from the drop-down menu.
- Add the columns to the chart shelf as shown below,
- X-axis: Customer Name
- Y-axis: Monetary Value with Sum function.
- Click Generate Graph and change the chart type to bar chart.
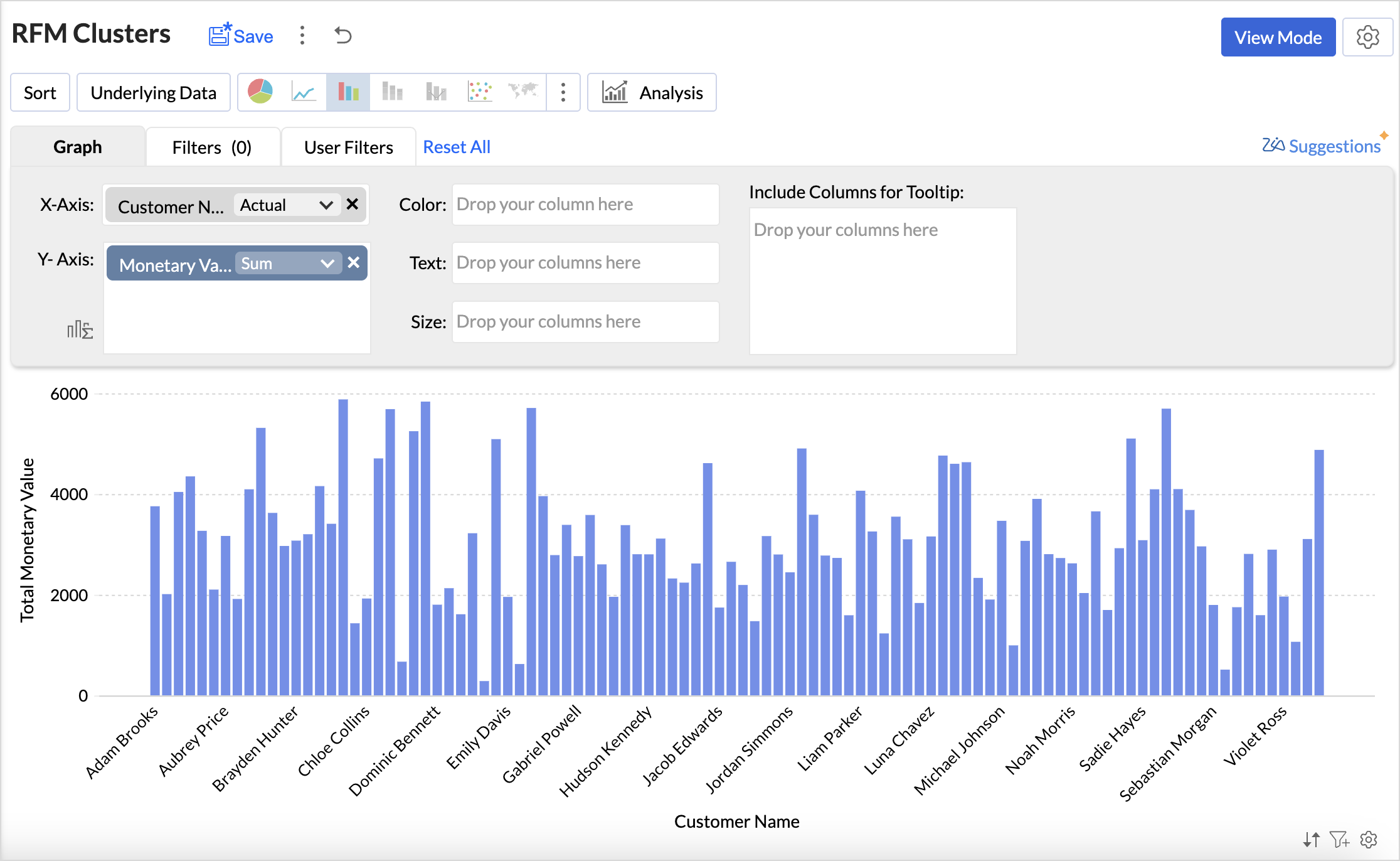
- Click the Analysis icon and select Cluster Analysis > Add Clusters.
- The Model is chosen automatically based on the columns dropped in the shelves.
- By default, the columns dropped in the shelves (Monetary Value) are selected as factors. Click the drop-down icon to include Recency and Frequency columns as factors.
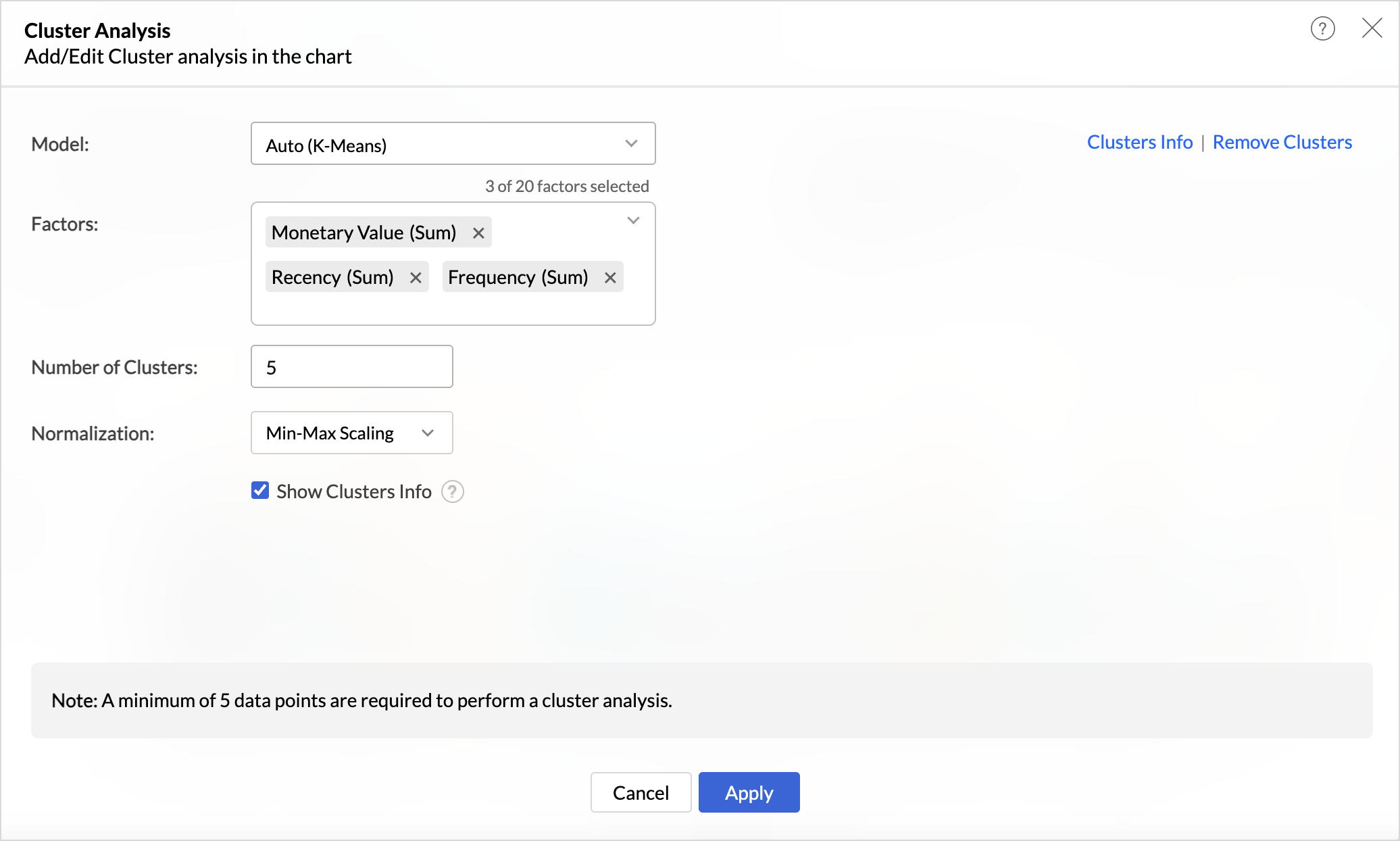
- The number of clusters is determined automatically but can be adjusted based on business needs and specific customer segmentation goals to ensure optimal categorization.
- Choose the Normalization method to prevent values of high ranges from dominating the results. For instance, Recency (measured in days) and Monetary Value (measured in currency) have different scales, and normalization ensures a balanced contribution from each metric.
- Click Apply.
4. Export Clusters Data
Once the customer profiles have been segmented using cluster analysis, Export the Current view in the preferred table format to build more data visualizations to understand the clusters.
Build an RFM Analysis Dashboard
The RFM analysis dashboard provides a comprehensive view of customer behavior. Let's look at the steps involved in building this dashboard.
1. Import the Clusters Data
Import the downloaded clusters table back into Zoho Analytics using the files option as given below.
- Click the New icon on the side navigation panel and choose New Table/ Import Data.
- Select files and choose the Clusters Table to import and click Next.
- A data preview will be displayed; verify the data types of columns and click Create.
2. Create Reports to Understand the Characteristics of the Clusters
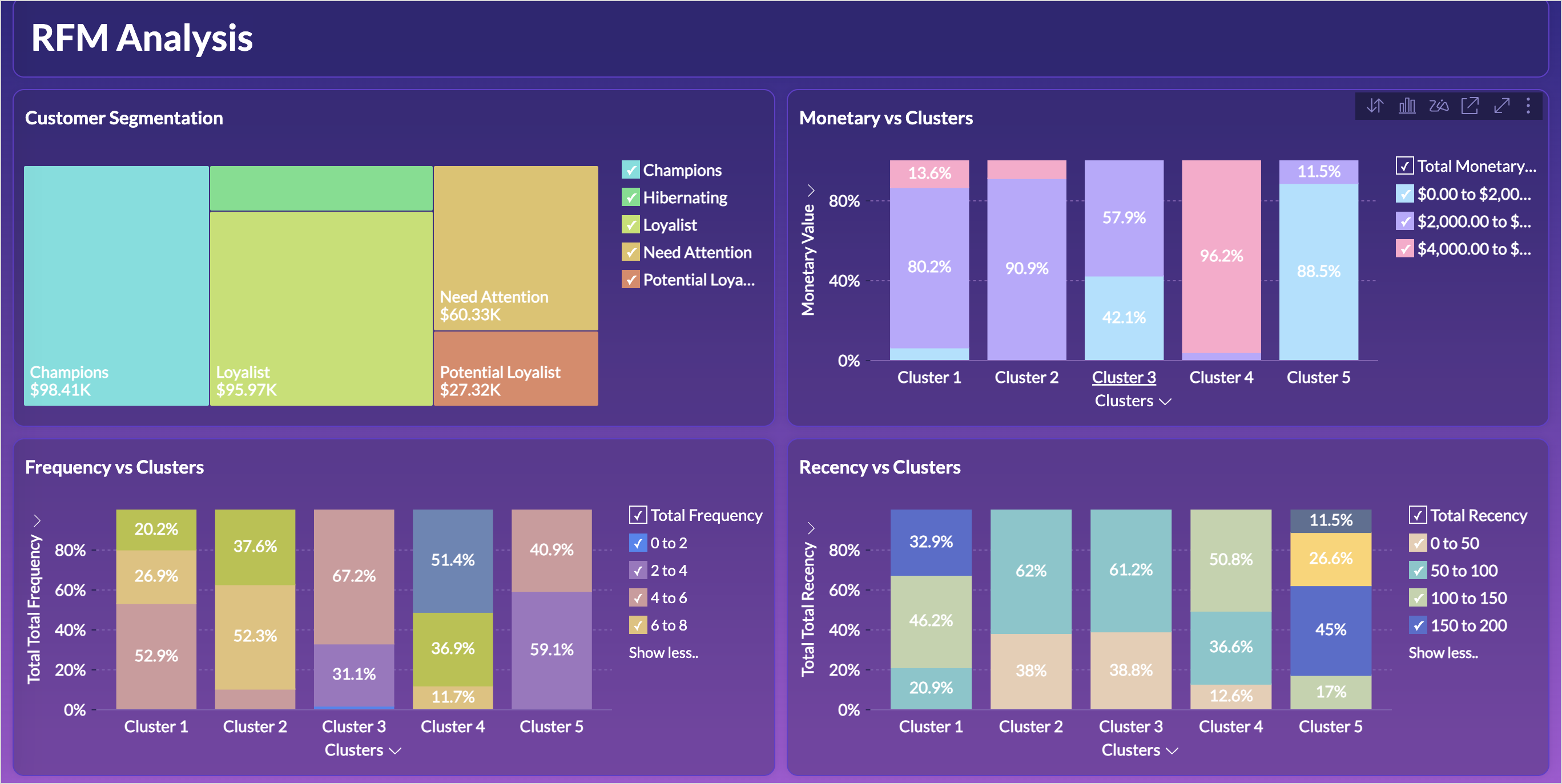
While the data is clustered, understanding the characteristics of each cluster is what enables businesses to take strategic actions. This includes identifying which customers need targeted marketing, personalized engagement, or retention efforts. Recognizing patterns within clusters provides insights into customer behavior, which is essential for optimizing marketing campaigns, improving retention strategies, and enhancing customer experience.
The below reports help understand the distribution of customers across different monetary value, recency and frequency segments within each cluster.
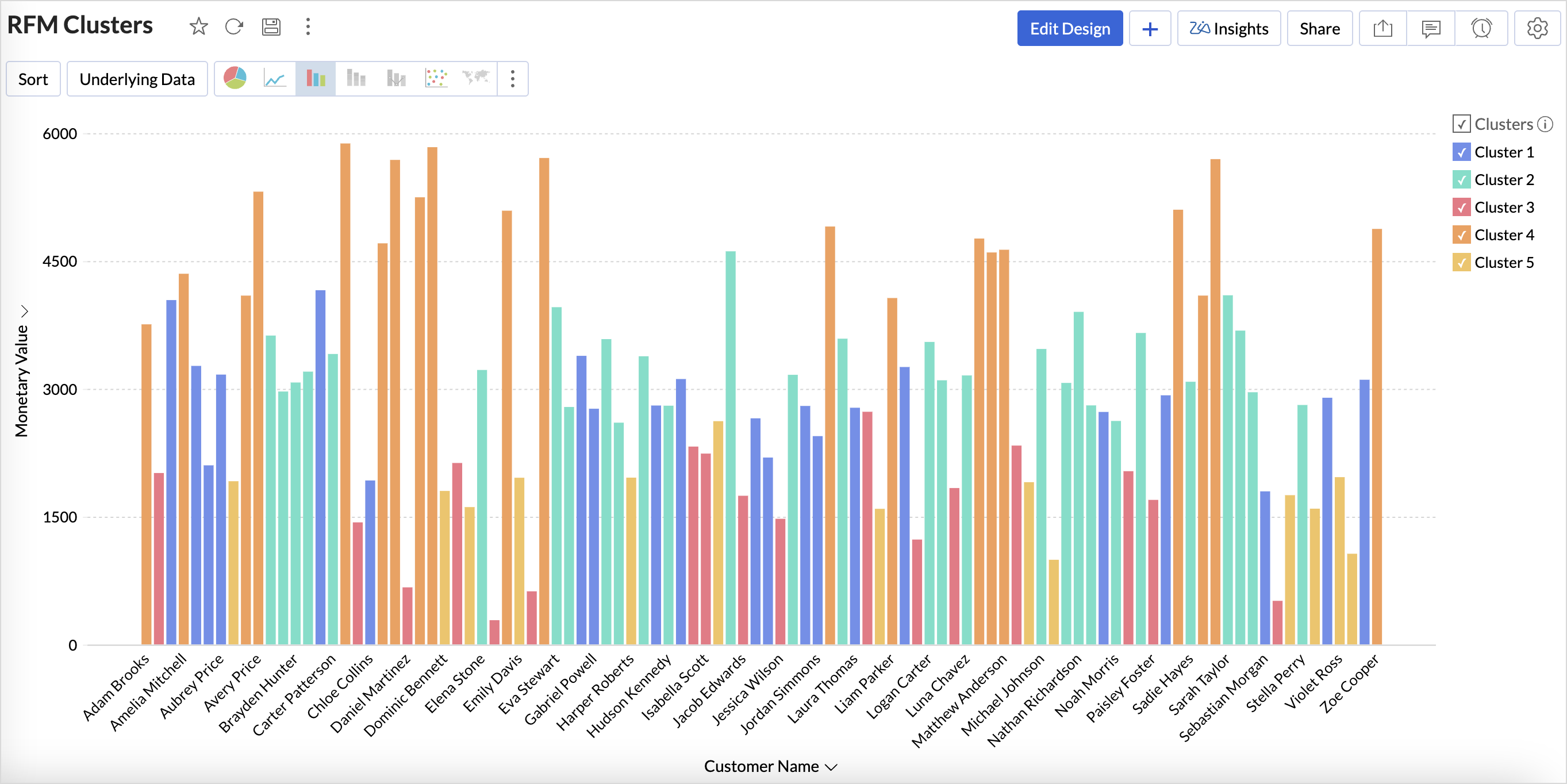
Clusters vs Monetary Value
- Access the cluster table (imported data) and click the new icon > chart view.
- Drag and drop the columns as given below:
- X-axis - Clusters
- Y-axis - Monetary Value with the Count function.
- Color - Monetary Value with the Actual Range function.
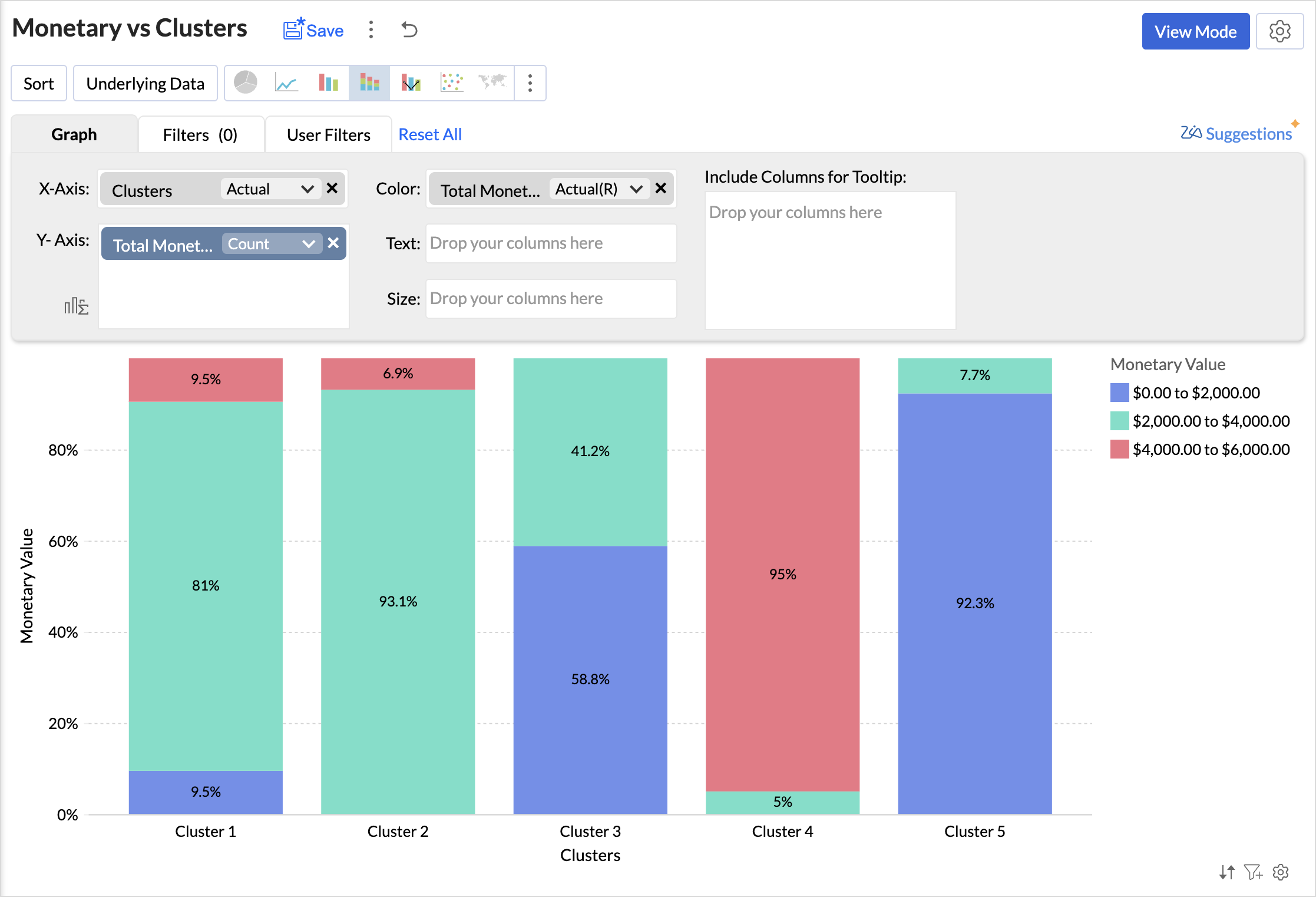
Analyzing the chart, we can infer that,
- Cluster 1 consists of a diverse group of customers spanning all spending levels.
- Cluster 2 includes moderate to high spenders who contribute significantly to revenue.
- Cluster 3 comprises low to mid-range spenders, often occasional buyers.
- Cluster 4 represents high-value customers with premium spending habits.
- Cluster 5 consists primarily of low spenders with minimal purchasing activity.
You can similarly create reports to know about the distribution of customers for the Recency and Frequency metrics.
The below table lists the characteristics of clusters
|
Cluster
|
Cluster Classification
|
Recency
|
Frequency
|
Monetary
|
Recommended actions
|
|
Cluster 1
|
Needs Attention
|
100 to 150 days
|
Low to Moderate
|
Diverse spending
|
Re-engagement campaigns, discounts, or reminders to encourage repeat purchases.
|
|
Cluster 2
|
Loyalist
|
0-50 (Highly Active)
|
High
|
Consistent moderate-to-high spenders
|
Loyalty programs, exclusive deals, early access to new products to maintain engagement.
|
|
Cluster 3
|
Potential Loyalist
|
0-50 (Active)
|
Low to Moderate | Budget-conscious, occasional buyers | Cross-selling, personalized recommendations, and value-based promotions. |
|
Cluster 4
|
Champions
|
100-150 (Inactive)
|
Moderate to High (Frequent buyers)
|
High spenders
|
VIP experiences, personalized services, and premium offers to retain and enhance their spending.
|
|
Cluster 5
|
Hibernating
|
Mostly inactive or infrequent
|
Low
|
Minimal spending
|
Win-back campaigns, incentives, special discounts, and targeted ads to regain interest.
|
Based on the above table, you can give specific labels to the clusters using the bucket columns option.
RFM Dashboard
Limitations & Considerations of RFM Analysis
While RFM analysis is a powerful customer segmentation tool, businesses should be aware of certain limitations and factors that can influence results:
- Data Freshness and Relevance: RFM analysis relies on transactional data, making the freshness and relevance of this data crucial for accurate customer segmentation. Setting up automated data imports ensures real-time updates, reducing the risk of working with stale data.
- Seasonal Variations: Customer purchasing behavior often fluctuates due to seasonal trends, holidays, and industry-specific cycles, which can impact RFM scores and lead to misleading segmentation if not accounted for properly. Instead of analyzing only recent months, compare customer behavior for the same period in previous years to detect true engagement patterns.
Topic Participants
Nisha Angel J
Hammer Group
Juan
Sticky Posts
What's New in Zoho Analytics - January 2026
Hello Users! We are starting the year with a strong lineup of updates, marking the beginning of many improvements planned to enhance your analytics experience. Explore the latest improvements built to boost performance, simplify analysis, and help youWhat's New in Zoho Analytics - November 2025
We're thrilled to announce a significant update focused on expanding your data connectivity, enhancing visualization capabilities, and delivering a more powerful, intuitive, and performant analytics experience. Here’s a look at what’s new. Explore What'sWhat's New in Zoho Analytics - October 2025
Hello Users! We're are back with a fresh set of updates and enhancements to make data analysis faster and more insightful. Take a quick look at what’s new and see how these updates can power up your reports and dashboards. Explore What's New! ExtremeWhat’s New in Zoho Analytics – September 2025
Hello Users!! In this month’s update, we’re raising the bar across multiple touchpoints, from how you bring in data, plan and track projects to how you design and brand your dashboards. We’ve added the all-new Gantt chart for project visualization, expandedAnnouncing Agentic AI - Ask Zia!
We are delighted to roll out the new agentic AI capabilities in Ask Zia, where every stage of the BI workflow is assisted by AI. With a human-in-the-loop approach, Ask Zia ensures that you’re in command of the decision, while AI handles the complexity.
Recent Topics
What's New in Zoho Billing | January 2026
Excited about the latest enhancements in Zoho Billing? Our January updates bring an intelligent AI assistant, smarter subscription management, and improved tax compliance, saving you time and reducing manual work. Dive into the details below to see howZoho Books Sandbox environment
Hello. Is there a free sandbox environment for the developers using Zoho Books API? I am working on the Zoho Books add-on and currently not ready to buy a premium service - maybe later when my add-on will start to bring money. Right now I just need aMulti-currency and Products
One of the main reasons I have gone down the Zoho route is because I need multi-currency support. However, I find that products can only be priced in the home currency, We sell to the US and UK. However, we maintain different price lists for each. ThereCliq iOS can't see shared screen
Hello, I had this morning a video call with a colleague. She is using Cliq Desktop MacOS and wanted to share her screen with me. I'm on iPad. I noticed, while she shared her screen, I could only see her video, but not the shared screen... Does Cliq iOS is able to display shared screen, or is it somewhere else to be found ? RegardsCOQL API in JS Widget only pulling 200 records
Hello! We've been building a custom homepage widget using the Zoho JS SDK, and it seems that this https://help.zwidgets.com/help/latest/ZOHO.CRM.API.html#.coql only allows 200 records. I thought the limit was 2000 for COQL queries, but am I mistaken?Passing the CRM
Hi, I am hoping someone can help. I have a zoho form that has a CRM lookup field. I was hoping to send this to my publicly to clients via a text message and the form then attaches the signed form back to the custom module. This work absolutely fine whenPaid Support Plans with Automated Billing
We (like many others, I'm sure) are designing or have paid support plans. Our design involves a given number of support hours in each plan. Here are my questions: 1) Are there any plans to add time-based plans in the Zoho Desk Support Plans feature? TheDo buttons and vba msgbox work on mobile, specifially the iPhone zoho sheets app?
In Zoho sheets on the web, I inserted a button and assigned a VBA macro to it. It pops up a msgbox with some text. When I go onto the iPhone mobile zoho sheets app, the button is there. When I click on that button, the spinning asterisk appears for aDifferent form submission results for submitter and internal users
I'm looking for suggestions on how to show an external submitter a few results while sending internal users all the results from the answers provided by the external user. The final page of our form has a section with detailed results and a section withColumn letter from number
Hello, I am trying to select a cell and i have the column number. How do i do this or is there a way of getting the letter from the number? Thank youHelp Desk Services Solution
I am here looking for Help Desk services solution for organization. I also searched this on many different website and found many solutions. We are bit confused to which one to choose. One of my friend suggest me this platform, and i am hoping i willFacing Issues with Sites Mobile font sizes
my page renediaz.com is facing issues mobile view, when i try to lower font sizes in home page, instead of changing the size, it changes the line spaceZOHO Payroll Canada
Any plans on the roadmap for Canada?Remove 'This is an automated mail from Zoho Sign' in footer
Hi there, Is it possible to remove or change the text under the e-mail templates? I can't figure out how to do that: Would love to hear from you. Kind regards, TristanFormatting and slow
Creating campaigns are difficult. I'm fairly computer literate but some of the way Zoho Campaigns formatting works is painful. Images fail to upload or are very slow. To top it off, syncing the contacts is a pain as well as temperamental links to create Segments. At this rate I'm afraid we might need to migrate back to Mailchimp.Default Ticket View - Table?
Guys, We mostly use the table view to queue tickets. Maybe I am missing it - but how can I set that view as 'default" for all our agents? Thanks JVBoost your Zoho Desk's performance by archiving tickets!
The longer your help desk operations are, the more likely it is to accumulate tickets that are no longer relevant. For example, ticket records from a year ago are typically less relevant than currently open tickets. Such old tickets may eventually leadPaste emails to create segment
We are moving over from Mailchimp to ZOHO. However Mailchimp allows me to create a segment by pasting in emails from excel (or importing a .csv) can I do the same in Mailchimp?Getting the Record ID of a form once it is submitted - so that form can be edited later
In Zoho Forms, where can I access the record ID of a form once the form is submitted? - Record ID is not available in webhook payloads - It is not available to form fields, including in formulas - It is not available as a parameter in a thankyou pageAuto-Generate Line Numbers in Item Table Using HTML & CSS Counters (Zoho Books & Zoho Inventory Custom Templates)
<div> <style> /* Start counter from 0 inside tbody */ tbody#lineitem { counter-reset: rowNumber; } /* Increment counter for each row */ tbody#lineitem tr { counter-increment: rowNumber; } /* Show counter value in first column */ tbody#lineitem tr td:first-child::beforePossible to define default font and size in Zoho Campaigns?
Is it possible to define a default font (font, size and colour) for the text, H1 and H2 in Zoho Campaigns? For example: In a campaign, I add a text block, and the text is automatically century gothic, size 11, grey (6f6f6e) by default? Thank you!Zoho Sites - General Feedback
Hi Everyone-- Quick question for discussion: is it me or is working with Zoho Sites like entering the Twilight Zone? I've built many sites over the years, but this platform seems impossible. I've spent an entire day and a half trying to get a simple one-colorFile Upload field not showing in workflow
Hi, I have added a field on Zoho CRM. I want to use it in a workflow where that particular field is updated based on another field, however it is not showing up in the field list to select it in the workflow. Why is this please?You cannot send this email campaign as it doesn't have any eligible contacts in the selected mailing list. You can try adding contacts or choose other mailing lists.
please helpStrengthening the capabilities of CommandCenter in Zoho CRM Plus
When you look at the prospect-to-customer journey in most businesses 10 to 15 years ago, it was relatively straightforward. Many of us remember walking into a store, sharing our requirements with a sales associate, reviewing a few options, and makingWorld date & time format
Hello, Is there a timeline to get the worldwide used date and time format ? I mean not the american one... I mean day month year, and 24 hours clock. RegardsHow can Data Enrichment be automatically triggered when a new Lead is created in Zoho CRM?
Hi, I have a pipeline where a Lead is created automatically through the Zoho API and I've been trying to look for a way to automatically apply Data Enrichment on this created lead. 1) I did not find any way to do this through the Zoho API; it seems likeAnnouncing Kiosk 1.1 - Customize screen titles, configure new fields & actions, use values from your Kiosk to update fields, and more.
Hello all We are back again with more enhancements to Kiosk. So what's new? Enhancements made to the Components Add titles for your Kiosk screens and adjust its width to suit your viewing preferences. Three new fields can be added to your screen: Percentage,Any recommendations for Australian Telephony Integration providers?
HI, I am looking for some advice on phone providers as we are looking to upgrade our phone system, does anybody have experience with any of the Australian providers that integrate with CRM Telephony? So far we are looking at RingCentral and Amazon Connect, and would love to hear feedback on any of the other providers you might have tried. Thank youCRM Cadences recognise auto-responses
I have leads in a Cadence. I get an auto-responder reply "I'm out of the office..." Normally Cadences seems to know that isn't a real reply and keeps the lead enrolled in the cadence. However, today, Cadences has UNENROLLED a Lead who sent an auto-reponseZoho Campaigns Workspaces
Hi, I’m currently working on a Zoho CRM + Zoho Campaigns setup for a franchisee-based organization, where each franchise must only see and use its own contacts. At the moment, franchisees cannot properly access their contact lists in Zoho Campaigns unlessLimited System because of Limited Number of Fields for Car Dealership
Dear Zoho Support, we want to have all the information about a car inside of a car record. We want to have Zoho CRM as our single source of truth for our data, but the limited number of fields are not allowing that. The data consist of: technical dataAutomatically Update Form Attachment Service with Newly added Fields
Hi, When I have a Form Setup and connected to a 3rd Party Service such as OneDrive for Form Attachments, when I later add a new Upload Field I have to remove and redo the entire 3rd Party Setup from scratch. This needs to be improved, such as when newZoho CRM for Everyone's NextGen UI Gets an Upgrade
Hello Everyone We've made improvements to Zoho CRM for Everyone's Nextgen UI. These changes are the result of valuable feedback from you where we’ve focused on improving usability, providing wider screen space, and making navigation smoother so everythingNewsletter in multiple languages
Hi We are planning on starting to use Zoho Campaigns for our newsletters. Since we send our newsletters in three languages, I would need the "unsubscribe page" and other pages related to the NL (Thank you page and so on) to be available in different languagesFixed assets in Zoho One?
Hi, We use Zoho Books and have the fixed asset option in it. I started a trial for Zoho One and I do not see that as an option. Is the books that is part of zoho one equivalent to Zoho Books Elite subscription or is it a lesser version? Thanks, MattSet Default Status of Assembly to "Assembled" When Entered in UI
I've just discovered the new "confirmed" status of Assemblies within Inventory. While I understand the intent of this (allowing for manufacturing planning and raw material stock allocation), it was initially confusing to me when manually entering someI need to Record Vatable amount and non vatable amount separately in zoho books in a single line
I need to Record Vatable amount and non vatable amount separately in zoho books in a single line give me the customisation option and in invoice copy to customer the total amount should be inclusive 5%vat and no need to show the vatable and non vatableSort Legend & stacked bar chart by value
I'd love to see an option added to sort the legend of graphs by the value that is being represented. This way the items with the largest value in the graph are displayed top down in the legend. For example, let's say I have a large sales team and I createScanned Doc - selecting Item overwrites Rate
I have a Vendor Invoice which was uploaded to Documents. I select Add To > New Bill. The OCR is actually quite good, but it is reading an Item Description instead of an Item Number. I remove the description and select the correct Item Number... and itNext Page