Creating and authorizing connections
 This help page is for users in Developer Console version 6. If you are using the older version (Developer Console 5), click here. Find out your Developer Console version.
This help page is for users in Developer Console version 6. If you are using the older version (Developer Console 5), click here. Find out your Developer Console version.1. What does this page cover?
Learn how to create a connection and how to authorize them in Developer Console for connecting your application with Zoho and third-party services. Before you proceed, you can learn more about Connections.

2. Availability
Can be created and managed only by the super admin and developers. The clients who access these applications in Zoho Creator can only authorize and access these installed connections.
3. Steps to create a connection
In the Zoho Developer Console, developers can configure connections to link their applications with external cloud services that can be used by clients when apps containing these connections are distributed. The process comprises two main steps: creating the connection with the necessary details and testing it in the development or stage environment before distributing the application. The clients installing the application containing a connection in their Zoho Creator account need to authorize it before use.

Note:
- Developer Console only supports built-in connectors.
- In the Developer Console, connections can be authorized by the super admin or developers in the development or stage environment for testing. For users of the installed app in Creator, depending on the type of connection chosen, the super admin, admin, or the logged-in users, must authorize the connections to ensure they function within the application.
Follow these steps to create and authorize a connection:
1. Navigate to the Microservices section in the left pane and click + Create New.

Note: When importing an application with an existing connection, a duplicate connection is created using a unique name and link name to maintain one-to-one mapping. The following naming format is used, <old-connection-name>_copy.
3. Upon selecting the connector, a popup will appear. The Connection Name will be auto-generated on choosing the connector, this can be edited by clicking the box.
If there are multiple connections with the same connector then the naming format will be as follows,
<service-name> [space] Connection <sequence>.
If there are multiple connections with the same connector then the naming format will be as follows,
<service-name> [space] Connection <sequence>.

4. Choose the level of authorization in the popup that follows. You can select the authorization level for clients accessing the connection as follows:
- Administrator: When this option is selected, only super admins, admins, and developers who install the application have the authority to authorize the connection. Regular users or non-administrative roles cannot authorize the connection but can use it through admin authorization, making the connection an admin connection.
- Logged-in User: If this option is chosen, any logged-in user who installs the application, regardless of their role, can authorize the connection. Unlike admin connections, these connections can hold individual authorization for all logged in users and can perform the integrations based on the authorization of the user who executes it. This means that super admins, admins, developers, and any logged-in user has the ability to grant authorization for the connection, making the connection a logged-in user connection. Logged-in user connections can be created only for limited built-in connectors.

Note: In the Developer Console, super admins and developers can authorize a connection regardless of the authorization level for testing it in the development or stage environment.
5. Configure the credentials for OAuth2 type connectors by selecting scopes for the connection. You can either select All Actions or limit the connection to specific actions based on your needs.

Note:
- If non-OAuth type connector is selected, then the users can proceed with the authorization without configuring the credentials.
- When selecting All Actions, all modules under the chosen service will be included, and you won’t be able to deselect them.
6. By default, the connection applies the same authorization across all environments, ensuring easier setup. To use a unique authorization for each environment, check the Use different authorizations for each environment box.

Note: The development & stage environment authorization is applicable for developers in Developer Console only. For the clients using the installed connection, only the production environment authorization will be available.
7. Click Create and Authorize.
8. Enter the authorization credentials in the popup. If using different authorizations, select the applicable environments.
9. Click Authorize. The created connection will now be prompted to be authorized for use. Follow any prompts for OAuth or third-party authorization.
Once the connection is authorized, it’s ready for use within your applications. You can edit the connection from the Connection Details page. Before you distribute the app to your clients (Marketplace or privately), you'll need to publish the connections changes to the Stage environment.
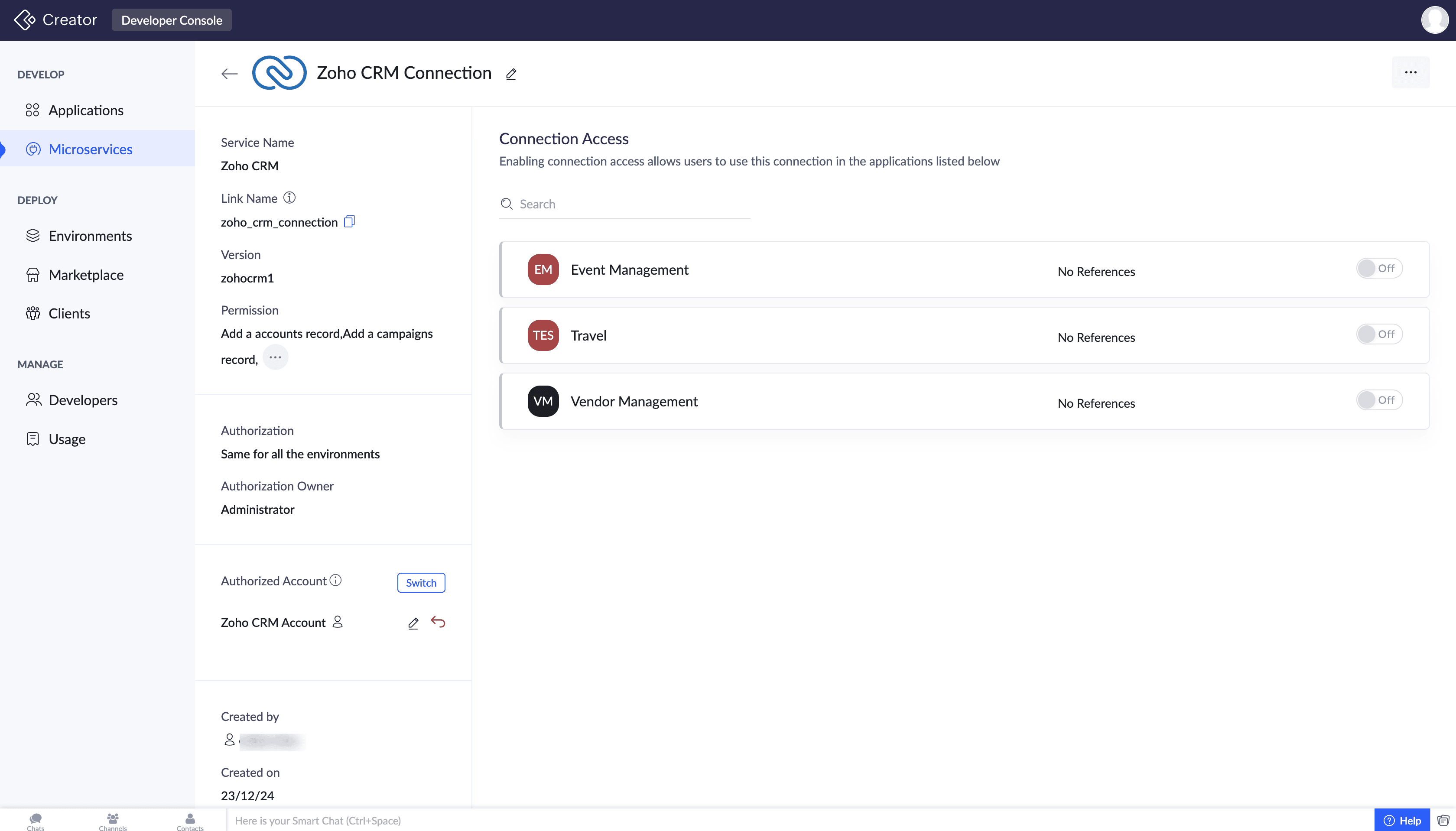

Note: The credentials required depend on the authentication type used by the external service (OAuth2, API key, etc.). Built-in connectors have pre-configured parameters; you will only need to provide the necessary credentials.
Changes to a connection can be published to the Stage environment only alongside its referenced components in the application.
3.1 Differences in authorization
- OAuth2 authentication: Services like Zoho CRM and Salesforce use OAuth2 authentication. When you click Authorize, you will be redirected to the service’s authorization page to approve the requested permissions.
- Basic authentication: Services like Zoho Projects require a username and password (auth token). When creating a connection, these parameters are configured, and the user provides credentials during authorization.
- API Key authentication: Services like Twilio require an API key, which is entered during connection setup.
4. Points to note
- In the Developer Console, connections are created with necessary details and authorized by super admins or developers for testing.
- Connections can only be published to the Stage environment along with the components they are referenced in.
- Clients must authorize connections when installing the application in their Zoho Creator account.
5. Related links
What's next
Previous step
What's next
After learning about creating and authorizing a connection, the next step is to see how to manage these connections effectively.
Previous step
Zoho CRM Training Programs
Learn how to use the best tools for sales force automation and better customer engagement from Zoho's implementation specialists.
Zoho DataPrep Personalized Demo
If you'd like a personalized walk-through of our data preparation tool, please request a demo and we'll be happy to show you how to get the best out of Zoho DataPrep.
Centralize Knowledge. Transform Learning.
All-in-one knowledge management and training platform for your employees and customers.
New to Zoho Writer?
You are currently viewing the help pages of Qntrl’s earlier version. Click here to view our latest version—Qntrl 3.0's help articles.
Zoho Sheet Resources
Zoho Forms Resources
New to Zoho Sign?
Zoho Sign Resources
New to Zoho TeamInbox?
Zoho TeamInbox Resources
New to Zoho ZeptoMail?
New to Zoho Workerly?
New to Zoho Recruit?
New to Zoho CRM?
New to Zoho Projects?
New to Zoho Sprints?
New to Zoho Assist?
New to Bigin?
Related Articles
Understanding connections
This help page is for users in Creator 6. If you are in the older version (Creator 5), click here. Know your Creator version In a nutshell Connection is a secure setup which handles the authorization process of connecting from Creator to other Zoho ...Managing connections
This help page is for users in Creator 6. If you are in the older version (Creator 5), click here. Know your Creator version. What does this page cover Learn to manage the connections you have created for integrating other Zoho or third-party ...Creating and authorizing connections
This help page is for users in Creator 6. If you are in the older version(Creator 5), click here. Know your Creator version. What does this page cover Learn how to create a connection and authorize it to integrate with other third party services with ...Managing connections
1. What does this page cover? Learn about managing the created connections and the types supported in Developer Console for connecting your application with other services. 2. Availability Connections can be created and managed only by the super ...Connections in live and edit mode
What does this page cover Learn to view and manage connections in the live and edit mode of your Zoho Creator application. Click here to learn more about connections. Availability Connections: Are available only for paid plans of Creator Can only be ...
New to Zoho LandingPage?
Zoho LandingPage Resources















